Video Compression Artifacts vs. Noise: Key Differences
In the world of digital video, visual quality can make or break your content. Whether you're editing a cinematic short film, reviving old home videos, or uploading social media content, visual clarity is essential. But what happens when your footage looks blocky, grainy, or just plain bad?
Two common culprits of video degradation are compression artifacts and noise. Though they may appear similar at a glance, these issues have very different causes-and fixing them requires different approaches. In this guide, we'll break down the differences between artifacts and noise, explore their impact, and introduce AI-powered solutions that can restore your video quality with just a few clicks.
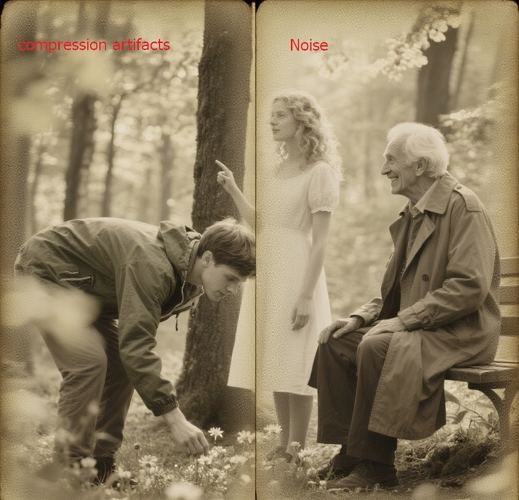

Part 1. Video Compression Artifacts vs. Noise
What Are Video Compression Artifacts?
Compression artifacts are unwanted visual distortions that occur when a video file is compressed using lossy codecs such as H.264 or MPEG-4. Compression helps reduce file size, but when too aggressive, it sacrifices visual detail-resulting in visible artifacts.
Common Types of Compression Artifacts:
- Blocking: Square patterns or visible grid lines due to macroblock compression.
- Banding: Unnatural color gradients, especially in skies or low-light scenes.
- Mosquito Noise: Flickering or buzzing around edges, especially in high-motion scenes.
- Color Smearing: Bleeding or loss of sharpness in colors and edges.
These issues are particularly noticeable in low-bitrate videos, such as online streams, compressed uploads, or exported footage with tight file size restrictions.
What Is Video Noise?
Video noise refers to random variations in brightness or color information in your footage. Unlike compression artifacts, noise typically originates during video capture, not encoding.
Common Causes of Noise:
- Low-light shooting conditions
- High ISO settings
- Small camera sensors
- Poor analog-to-digital conversion
Types of Video Noise:
- Luminance Noise: Grainy brightness variations.
- Chrominance Noise: Colored speckles, often red, blue, or green.
- Temporal Noise: Flickering grain that changes frame to frame.
Noise can give your video a gritty, unprofessional appearance. It's especially common in smartphone footage, webcams, and vintage analog recordings.
Key Differences Between Artifacts and Noise
Feature
Compression Artifacts
Video Noise
Cause
Lossy compression codecs
Poor lighting, sensor limits
Appearance
Blocks, banding, smearing
Grainy, random speckles
Pattern
Structured, repetitive
Random or semi-random
Common in
Streaming, downloads, exports
Night scenes, old footage
Fix Method
Deblocking, restoration algorithms
Denoising filters, AI enhancement
Part 2. What Do Noise and Comperssion Impact on Video Quality
Both noise and compression artifacts reduce visual fidelity, making your video appear cheap, unpolished, or even unwatchable. Artifacts tend to disrupt sharp edges and smooth gradients, while noise introduces unwanted texture and distraction.
This becomes a real issue when:
- You're editing videos for YouTube or film distribution.
- Archiving family footage or old memories.
- Trying to extract detail from security footage or digital archives.
Understanding which issue you're dealing with is crucial for choosing the right fix.
Part 3. How to Fix Compression Artifacts and Noise
The traditional way to fix compression artifacts and noises include:
- Manual Denoising: Available in software like Adobe Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve, but often requires fine-tuning and technical knowledge.
- Export Settings Optimization: Helps reduce compression artifacts, but doesn't fix existing damage.
- Third-Party Filters: Can denoise or deblock, but often introduce blur or soften detail.
These methods can be time-consuming, inconsistent, or produce limited results-especially when both noise and artifacts are present.
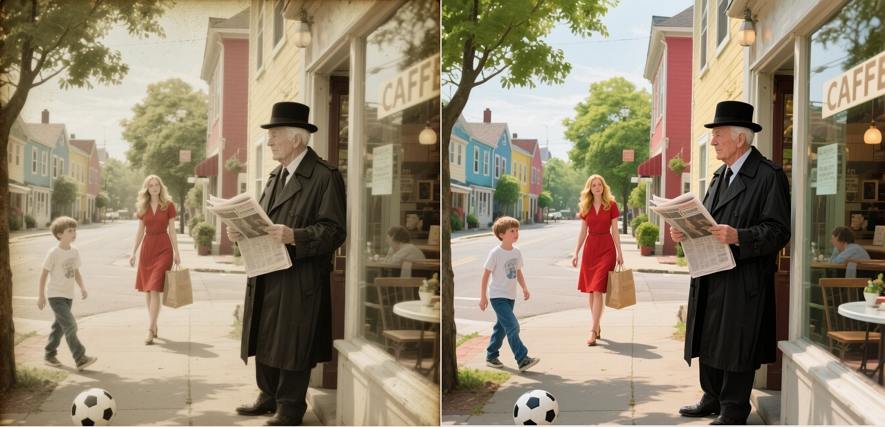
This is where modern AI video enhancement HitPaw VikPea comes in. Using advanced deep learning models, VikPea can analyze the video frame by frame to identify and fix both types of degradation-compression artifacts and noise-intelligently.
HitPaw VikPea provides:
- Supports multiple video types and formats including MP4, MOV, AVI, 3GP, etc.
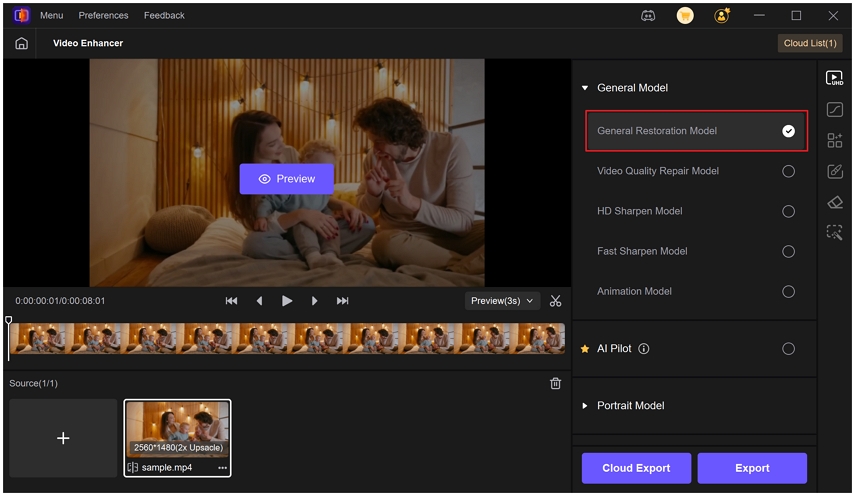
- Multiple AI models for different video types. For example, the General Restoration Model aims to fix compression damage and enhances old or low-res footage, the Video Quality Repair Model removes noise and recovers lost detail, and the Portrait Model specializes in restoring facial clarity and detail.
- User friendly interface, no technical skill required.
- Supports Batch Processing: Fix multiple videos at once.
- Exports videos up to 8K resolution

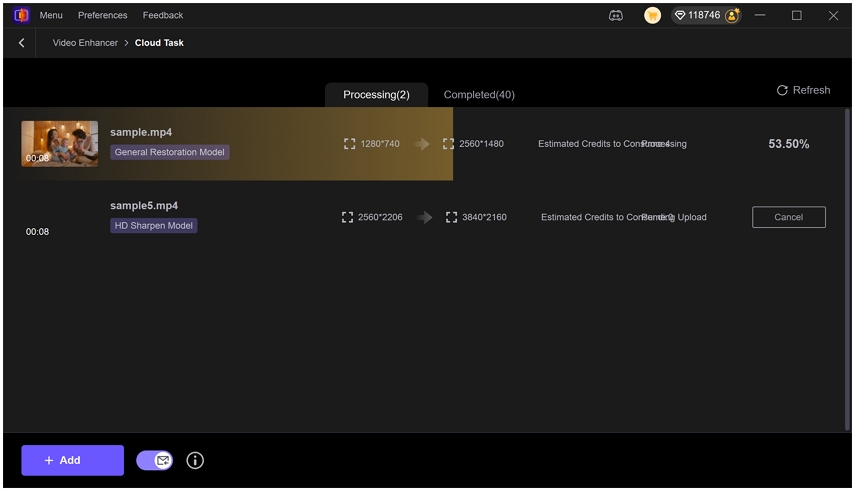
How to Use HitPaw VikPea to Restore Your Video
Here's a simple step-by-step process:
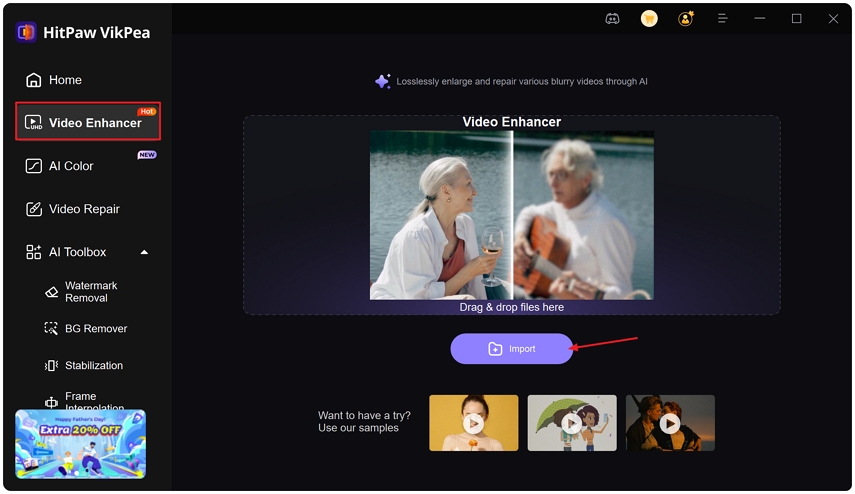
Step 1.Download and install the software on your PC or Mac. Open the program and import your video to the Video Enhancer interface.

Step 2.Choose an AI model based on your issue from the left panel.

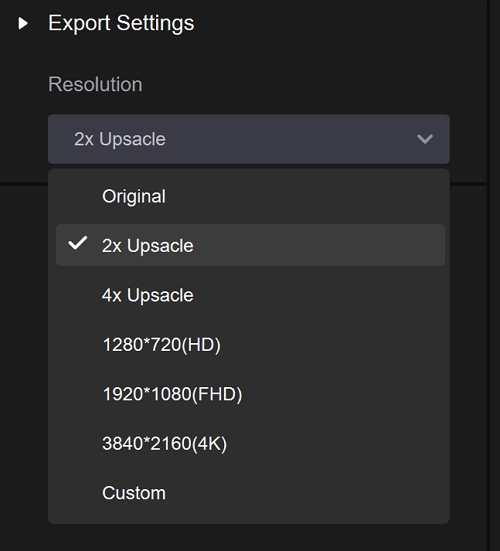
Step 3.In the Export Settings, the default quality is 4K. You can choose a desired resolution to export.

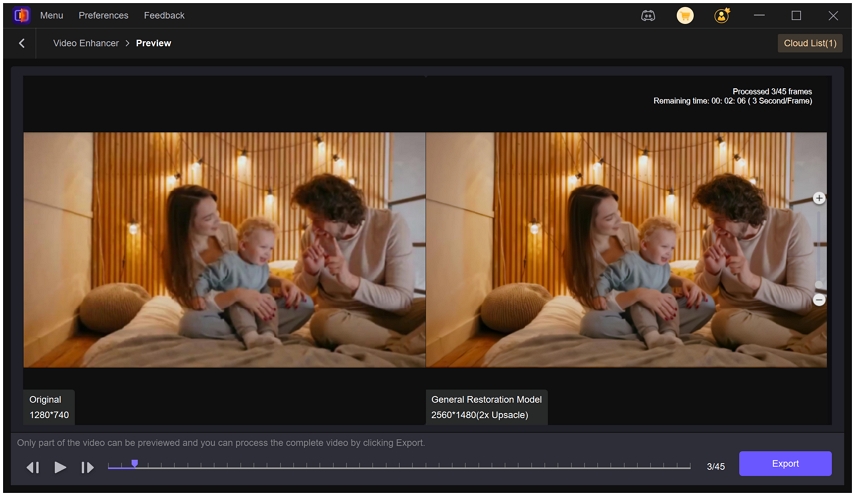
Step 4.Click Preview to see the before/after comparison.

Step 5.Click the Export button to export the video in your desired format and resolution.

FAQ Section
Q1. Can AI fix both compression artifacts and noise at once?
A1. Yes. AI tools like HitPaw VikPea offer dedicated models that can detect and correct both issues simultaneously.
Q2. Is video noise always a problem?
A2. Some filmmakers add grain intentionally for a filmic look. However, unintentional noise, especially in low-light footage, is typically unwanted.
Q3. How do I know whether my video has artifacts or noise?
A3. Artifacts often appear as square blocks or blurry edges, especially during fast motion. Noise looks like random grain, mostly in shadows or dark areas.
Q4. Does video upscaling help reduce compression artifacts?
A4. Upscaling alone won't fix artifacts, but when paired with AI restoration, it can significantly improve visual quality.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between video compression artifacts and noise is essential for video restoration and enhancement. While they may seem similar, their origins and fixes differ greatly. Fortunately, with the advancement of AI-powered video tools like HitPaw VikPea, both issues can be addressed in a single workflow.
Don't let low-light, compression, or poor-quality recording ruin your content. Let smart technology handle the heavy lifting-and bring your videos back to life.








 HitPaw Univd (Video Converter)
HitPaw Univd (Video Converter) HitPaw VoicePea
HitPaw VoicePea  HitPaw FotorPea
HitPaw FotorPea


Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Daniel Walker
Editor-in-Chief
This post was written by Editor Daniel Walker whose passion lies in bridging the gap between cutting-edge technology and everyday creativity. The content he created inspires the audience to embrace digital tools confidently.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles