Everything You Should Know About UV vs. Polarizer Filters
In today's photography, lens filters help control light before it hits the camera. Two common but often mixed-up types are the UV filter and the polarizer. Though they may look alike, each has a clear job and affects photos in different ways. A UV filter mostly guards the lens and slightly boosts image quality. It's not a creative tool, but more of a quiet helper.
A polarizing filter, however, actively changes how light reflects, cutting glare and deepening color. With input from The Artist Gallery and pros on LinkedIn, this piece looks at how both filters work. When used right, they can sharpen photos, enrich colors, and add a pro touch.
1. Understanding UV Filters
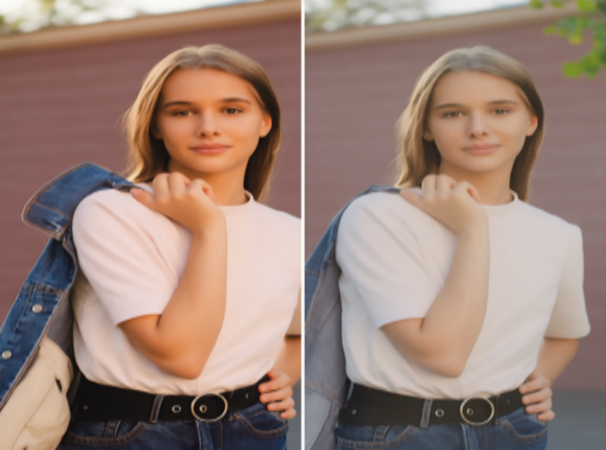

A UV filter is a clear glass disc that blocks ultraviolet light and protects the lens. In the film days, it reduced haze in high places or near the sea, where UV rays were stronger. It helped prevent overexposed or blue-tinted photos. Today, digital sensors don't need UV protection, but the filter is still useful.
The main benefit of a UV filter now is lens protection. It shields against scratches, dust, moisture, and fingerprints-things that can harm the lens surface. It also cuts some atmospheric haze, which helps with clarity in landscape shots. It doesn't change color or exposure, just gives a light boost to image sharpness.
Importantly, a UV filter is cheap to replace if it breaks, saving your real lens from damage. Some versions have multi-coating to reduce reflections and improve light flow, especially in bright settings.
UV filters are great for many uses. They're handy for outdoor, mountain, or aviation photography, where UV levels are high. Even in everyday shooting, they protect against dust and weather. That's why many photographers leave them on their lens full-time.
2. Understanding Polarizing Filters
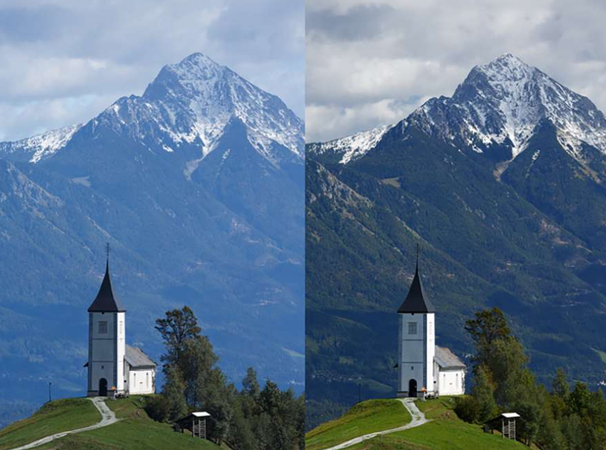

A polarizing filter is an essential tool for photographers, designed to enhance image quality through the manipulation of light.
Functionality
Polarizing filters work by reducing glare and reflections from surfaces like water and glass. They help to saturate colors, making skies appear deeper and foliage more vibrant.
Benefits
- Glare Reduction: By filtering out polarized light, these filters minimize reflections, improving clarity in outdoor shots.
- Color Saturation: They enhance the richness of colors, especially in landscape photography, making images more visually appealing.
- Sky Contrast: Polarizers can darken blue skies, making clouds stand out and adding depth to the scene.
Practical Applications
Polarizing filters are particularly useful in outdoor photography, such as landscapes, seascapes, and architecture. They are effective in situations where light is reflecting off surfaces, helping to achieve clearer and more striking images.
Considerations
While polarizing filters can significantly improve photos, they may require adjustments in exposure settings, as they can reduce the amount of light entering the lens. It's essential to experiment with different angles to achieve the desired effect.
In summary, polarizing filters are valuable assets for photographers looking to enhance image quality and control light effectively.
3. Key Differences Between UV and Polarizing Filters
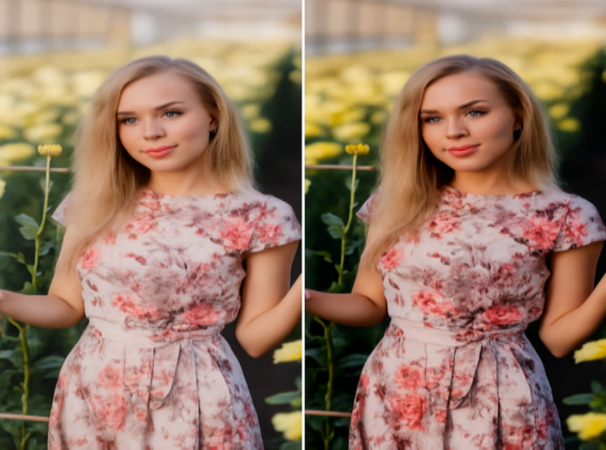

When comparing polarizing filters to UV filters, it's essential to understand their distinct roles:
Purpose
- UV Filter: Primarily protective, designed to shield your lens from dust, scratches, and moisture. It does not affect exposure or color, making it versatile for all lighting conditions.
- Polarizing Filter: A creative tool that enhances image quality by controlling reflections and boosting color saturation. It requires adjustment based on light and shooting angle.
Image Impact
- UV Filters: Provide minor improvements, typically noticeable in hazy conditions. They help reduce light haze but have minimal overall effect on image quality.
- Polarizing Filters: Can dramatically transform a photograph, turning a pale sky into a vibrant blue and adding depth to flat images. The impact is often striking and clear.
Cost
- UV Filters: Generally affordable, even high-quality multi-coated options are reasonably priced.
- Polarizing Filters: Tend to be more expensive due to additional glass layers and specialized coatings. However, investing in quality is crucial for both types.
4. How to Use UV Filters Effectively
Using a UV filter is straightforward. It screws onto the front of your lens like a lens cap or hood. Here's a quick overview of how to maintain and utilize it effectively:
Installation and Maintenance
- Installation: Simply screw the UV filter onto the lens front.
- Maintenance: Keep the glass clean with a microfiber cloth and a lens-safe cleaning solution.
To further reduce flare, some photographers use a lens hood in conjunction with the filter. A high-quality UV filter with an anti-reflective coating can help minimize flare, but cheaper or uncoated filters may still introduce issues.
Optimal Conditions
UV filters are most effective in outdoor environments with plenty of natural light and atmospheric haze. Ideal situations include:
- Mountaintop photography
- Seascapes
- Desert scenes
Although digital sensors are less sensitive to UV light compared to film, the slight enhancements in contrast and clarity make UV filters valuable. Their protective features also justify their use on many photographers' lenses.
Limitations
However, UV filters are not universally beneficial. In low-light or indoor settings, adding an extra layer of glass can slightly reduce sharpness or increase flare. Consequently, photographers working in controlled studio environments or under artificial light often choose to remove the UV filter.
5. How to Use Polarizing Filters Correctly
To use a polarizing filter successfully, it's important to understand both the filter itself and how it interacts with light.
Installation and Adjustment
A circular polarizer screws onto your lens and features a rotating ring. This ring allows you to adjust the strength and direction of the polarizing effect.
- Adjustment: While looking through the viewfinder or LCD, turn the ring to see changes in glare and contrast. The best results typically occur when your lens is at a 90° angle to the sun. Shooting directly toward or away from the sun diminishes the effect.
Exposure Considerations
A polarizing filter reduces light entering the lens by about 1.5 to 2.5 stops. As a result, you may need to make adjustments:
- ISO: Increase the ISO setting.
- Aperture: Open the aperture wider.
- Shutter Speed: Slow down the shutter speed.
Most cameras will adjust automatically, but if you're in manual mode, you'll need to compensate accordingly. In low-light situations, using a tripod can help prevent blur.
Common Mistakes
- Overuse: Applying too much polarization can lead to unnatural-looking skies or dark bands, especially with wide lenses (under 24mm on full-frame cameras).
- Dirty Filters: A dirty polarizing filter can reduce sharpness and cause ghosting effects.
Practice and Learning
To master the use of a polarizing filter, practice is key. Learn how light changes your scene and how to best utilize the filter to enhance your photographs. With experience, you'll be able to take full advantage of the polarizer's benefits.
6. Choosing the Right Filter for Your Needs
Choosing between UV vs polarizing filter depends on your specific photographic goals. For protection and minor environmental correction, a UV filter is an excellent, low-maintenance tool. For creative control over reflections and color saturation, a polarizer is unmatched. Consider your shooting conditions, subject matter, and artistic intent. If budget allows, owning both offers flexibility and full coverage of your photographic needs.
When selecting a filter, check your lens thread size, usually marked on the front of your lens with a diameter symbol (Ø). Opt for filters made from high-quality optical glass with multi-coating to prevent reflections and preserve image quality. Reputable brands include B+W, Hoya, Tiffen, and Kenko. It is also wise to avoid stacking filters unnecessarily. While you can combine a UV and polarizer, doing so may cause vignetting or increased flare, particularly on wide-angle lenses. Only stack filters when the benefits outweigh the drawbacks.
7. An Amazing App for Photo Enhancer: HitPaw Photo Enhancer
After capturing your images, you may want to enhance them further. HitPaw Photo Enhancer is an AI-powered tool designed to upscale and sharpen your photos automatically. It helps improve clarity, eliminate noise, and restore detail lost during shooting or compression. The tool is especially useful for outdoor images where the lighting was less than perfect, or when the filters didn't completely neutralize glare or haze.
8. Conclusion
In the polarising filter vs uv filter debate, it is clear that each has a unique and irreplaceable role. UV filters offer essential lens protection and slight enhancements in clarity. Their strength lies in simplicity and consistency. In contrast, a photography polarizing filter provides dynamic control over how your camera interacts with light, enabling bolder, more vivid images with fewer reflections and richer colors.
Both filters have earned a place in any serious photographer's gear bag. Knowing when and how to use each effectively is a mark of professionalism. Try both in different shooting scenarios to understand their strengths. You'll soon find they are not competing tools but complementary allies in your creative process.






 HitPaw Univd (Video Converter)
HitPaw Univd (Video Converter) HitPaw VoicePea
HitPaw VoicePea  HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)
HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)


Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Daniel Walker
Editor-in-Chief
This post was written by Editor Daniel Walker whose passion lies in bridging the gap between cutting-edge technology and everyday creativity. The content he created inspires the audience to embrace digital tools confidently.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles