WAV vs MP3: Key Differences in Audio Quality, File Size, and Usage
Audio formats shape how music sounds, how much storage it takes, and how easily files can be shared. The long debate of WAV vs MP3 comes down to one core trade-off between pristine quality and practical convenience. WAV is a lossless format that keeps every detail of the original recording, making it ideal for professionals, studios, and post-production work. MP3 is a compressed format designed for portability, streaming, and everyday listening. Understanding the differences between WAV file format vs MP3 helps creators, musicians, and listeners make better technical and creative decisions.
Part 1. WAV vs. MP3: Which one is Better?
When comparing WAV vs MP3, neither format is universally better because each serves a different purpose. WAV delivers studio-grade, lossless audio with maximum detail, making it superior for recording, editing, and archiving. MP3 prioritizes efficiency by reducing file size while maintaining acceptable sound quality, which makes it far more practical for streaming, sharing, and mobile listening across devices.
WAV vs MP3 Player Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | WAV (Waveform Audio File Format) | MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer III) |
|---|---|---|
| Compression | Uncompressed / Lossless | Compressed / Lossy |
| Quality | Perfect, bit-for-bit reproduction | Slightly reduced, some data removed |
| Bit Depth | Higher bit depth | Lower bit depth |
| File Size | Very large, about 10MB per minute | Small, about 1MB per minute at 128kbps |
| Editing | More flexible for editing and post-production work | Less flexible for editing and post-production work |
| Best For | Editing, mastering, and archiving | Streaming, podcasts, and casual listening |
| Metadata | Limited standardized support | Extensive ID3 tags for artist, title, art |
Part 2. What are the Key Differences Between WAV and MP3?
The main differences between WAV vs MP3 lie in compression, quality, and usability. WAV preserves every audio detail but creates massive files, while MP3 compresses sound to save space at the cost of some fidelity. This makes WAV ideal for professional workflows and MP3 better for everyday consumption, portability, and online distribution.
1. WAV vs MP3: Sound Quality
Sound quality is the most discussed factor in the MP3 vs WAV debate. Professionals care deeply about clarity, depth, and tonal accuracy, while casual listeners often prioritize convenience over perfection. Your playback system, headphones, and listening environment also influence how noticeable these differences really are.
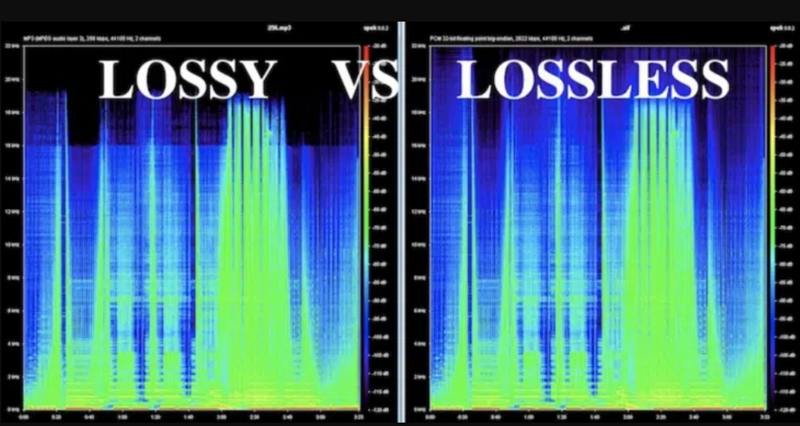
WAV offers lossless, full-range audio that keeps all original detail, dynamics, and depth. MP3 removes certain audio data that the human ear is less likely to notice, which can slightly reduce richness, especially in complex music or high-end equipment.
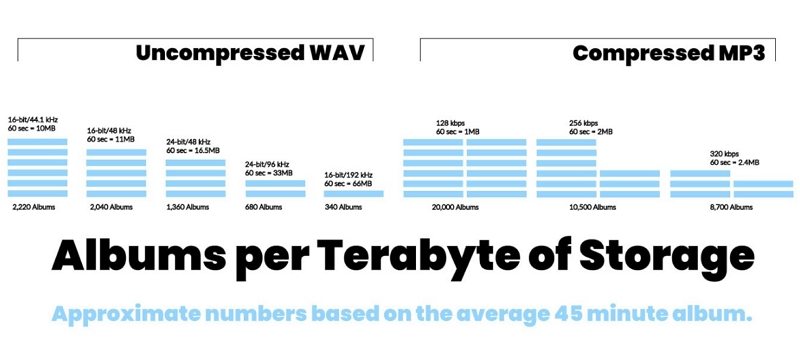
2. WAV vs MP3: Compression and File Size
Compression determines how much storage a file occupies and how easily it can be transferred. This is a major reason why WAV format vs MP3 is so widely debated in digital media and streaming industries.
WAV is uncompressed, meaning it keeps all audio data and results in very large files. MP3 uses lossy compression to shrink files dramatically, making it ideal for playlists, downloads, and online platforms.
3. WAV vs MP3: Bitrate and Codec
Bitrate affects how much audio data is processed per second, directly influencing clarity and detail. Understanding bitrate helps explain why some MP3 files sound better than others.
WAV typically uses high, fixed bitrates that preserve full fidelity. MP3 supports variable bitrates, allowing users to balance quality and file size, but lower bitrates can noticeably degrade sound.
4. WAV vs MP3: Workflow and Editing
Editors and producers handle audio differently depending on format choice. This is a key distinction in .WAV vs MP3 for creative professionals.
WAV is easier to edit, mix, and master because it contains complete, untouched audio data. MP3 can introduce artifacts and limitations that make advanced editing more challenging.
5. WAV vs MP3: Device Compatibility
Compatibility determines whether a file will play smoothly across devices, apps, and platforms. This matters greatly for everyday users.
MP3 is nearly universal and plays on almost all devices, apps, and platforms. WAV is widely supported but less practical for mobile storage and streaming.
Part 3. Pros and Cons of WAV and MP3
Every audio format has strengths and weaknesses depending on user needs. The choice between WAV file vs MP3 depends on whether quality or convenience matters more in a given situation.
Pros and Cons of WAV Format
Pros
- Perfect lossless audio preserves every original detail
- Best for professional music production and mastering
- Ideal for sound design, film, and studio recording
- No quality degradation during editing or re-saving
- Supports high bit depth and sample rates
Cons
- Extremely large file sizes require more storage
- Not ideal for streaming or sharing online
- Slower to transfer and upload
Pros and Cons of MP3 Format
Pros
- Very small file size saves storage space
- Works smoothly on almost every device
- Perfect for streaming and online sharing
- Fast downloads and easy distribution
- Supports rich metadata including album art
Cons
- Lossy compression reduces audio detail
- Not ideal for professional editing workflows
- Quality depends heavily on bitrate
Part 4. Which Audio Format Should You Choose: MP3 or WAV?
Choose MP3 if you need portability, streaming, and convenience, and choose WAV if you need maximum sound quality, professional editing, or archival storage. The best option depends on your goal, whether that is listening, sharing, producing, or publishing audio content.
Use MP3 If:
- You stream music on mobile devices
- You need small files for storage
- You share audio frequently online
- You create podcasts or playlists
- You prioritize compatibility over perfection
Use WAV If:
- You record music professionally
- You edit audio in a studio
- You archive high-quality masters
- You work in film or sound design
- You want the highest WAV vs MP3 quality
Special pick: All-in-One WAV and MP3 Converter
HitPaw Univd is an all-in-one media tool that supports audio conversion, playback, and editing. It helps users switch between formats like .WAV vs.MP3 smoothly while preserving quality. The software is beginner-friendly yet powerful enough for creators who need fast, reliable audio processing without complex technical steps.
- Converts audio between WAV, MP3, FLAC, and more formats
- Batch audio conversion saves time efficiently
- Built-in high-quality audio player for previewing files
- Supports trimming, cutting, and merging audio tracks
- Allows bitrate and sample rate customization
- Extracts audio from video with clean output quality
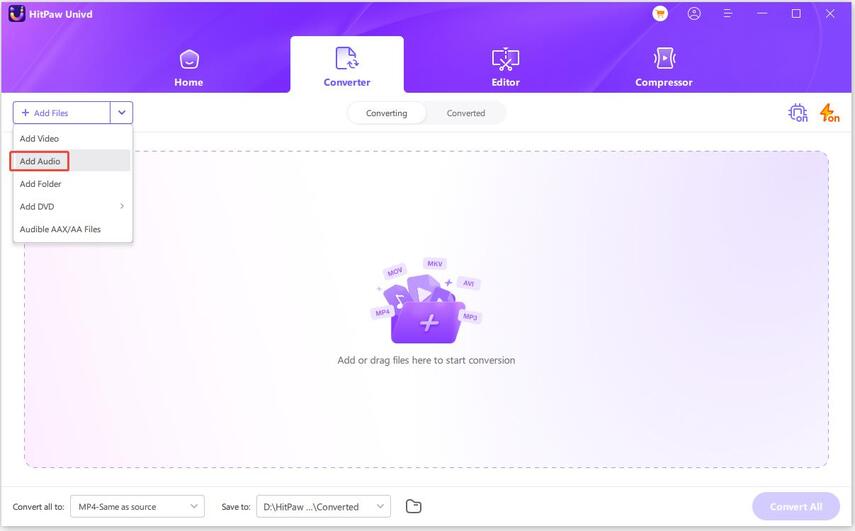
Step 1.Install HitPaw Univd on your computer, open the program, and go to the Converter section. Click Add Audio to import your file.

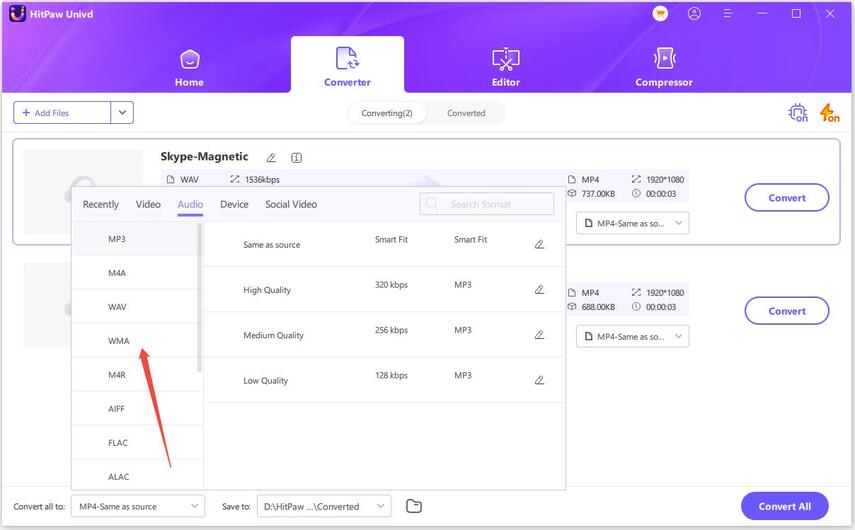
Step 2.Tap Convert All to and select your preferred output format such as MP3 or WAV.

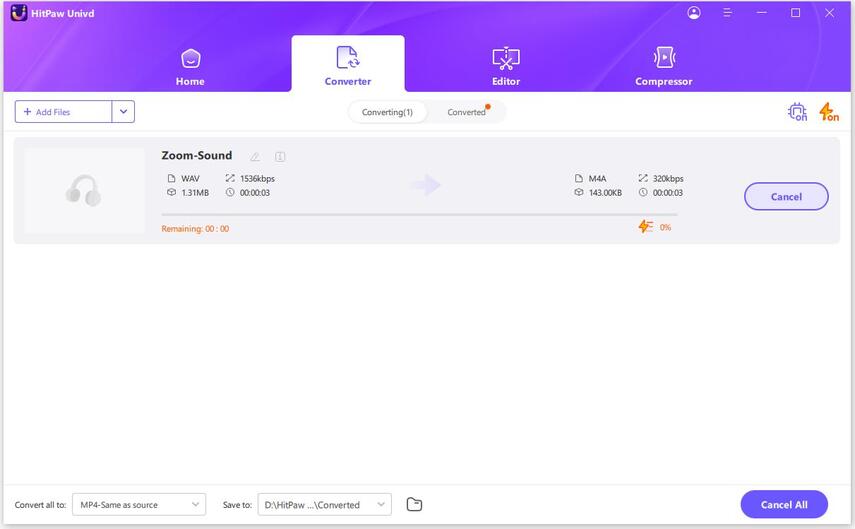
Step 3.Click Convert All to start processing. Once finished, find your files in the Converted tab.

WAV vs MP3 Frequently Asked Questions
WAV files take up significant storage space, making them impractical for mobile devices and streaming. They are slower to upload, harder to share, and often unnecessary for casual listening where MP3 quality is sufficient.
Export as WAV if you plan to edit, mix, or master audio professionally. Choose MP3 if your goal is sharing, streaming, or saving space, especially for podcasts or music playlists.
Spotify accepts high-quality files but ultimately streams in compressed formats. WAV is better for upload quality, while MP3 works fine for everyday listening within the app.
Yes, WAV delivers lossless, full-fidelity audio while MP3 removes some data through compression. This makes WAV superior in clarity, depth, and detail, especially on high-end audio systems.
Conclusion
The choice between WAV vs MP3 depends entirely on your purpose. WAV is unbeatable for professional audio work, recording, and archiving, while MP3 dominates streaming, portability, and everyday listening. Understanding MP3 vs WAV format differences empowers you to select the right tool for the right task, whether you are a creator, musician, or casual listener.
Leave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles