What Is HDR Tone Mapping? How Does It Work and Why We Need It?
High Dynamic Range (HDR) content delivers vivid highlights and deep shadows, but standard displays can struggle to reproduce its full range. This is where HDR Tone Mapping comes in. By intelligently compressing and reassigning brightness levels, HDR Tone Mapping ensures that every detail, from sunlit skies to dimly lit interiors, appears natural and richly detailed on your screen. Whether you're a photographer, filmmaker, or gamer, understanding HDR Mapping can elevate your viewing experience to new heights.
Part 1. What is HDR Tone Mapping?
HDR Tone Mapping is a process that transforms high dynamic range imagery so it can be displayed on devices with limited brightness and contrast capabilities. By mapping scene luminance values to the display's range, it preserves critical details while maintaining perceptual realism.

Essentially, HDR Tone Mapping adaptively adjusts highlights and shadows in each frame, ensuring that bright areas aren't blown out and dark regions retain visible texture. This technique bridges the gap between the high ranges captured by cameras or generated by graphics engines and the actual capabilities of consumer displays.
Part 2. Why We Need HDR Tone Mapping?
While HDR content offers a broader luminance gamut, not all screens can handle the full range captured by modern cameras or rendering pipelines. Without HDR Mapping, highlights may appear clipped and shadows murky, resulting in loss of visual fidelity. Tone mapping creates a compromise that accommodates both source material and display constraints, all while simulating how the human eye perceives light and contrast.
- Conflict between HDR content and standard display capabilities
- Simulation of human visual perception characteristics
- Preventing highlight clipping in bright areas
- Preserving texture and detail in dark regions
- Ensuring compatibility across different display devices
Part 3. How Does Tone Mapping Work?
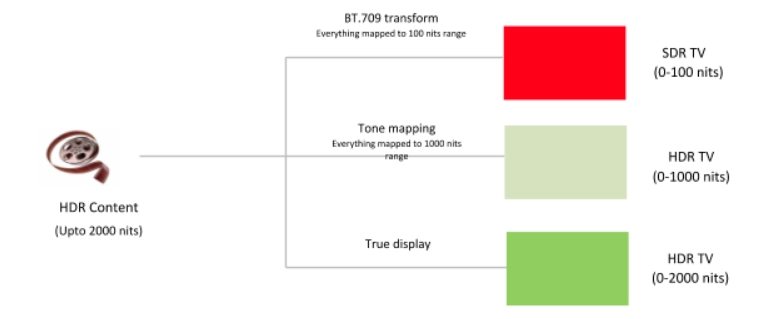
Tone mapping algorithms analyze the luminance distribution of each HDR frame and apply mathematical transformations to fit it within a display's dynamic range. There are global operators that apply the same curve to the entire image and local operators that adapt based on regional luminance. Through contrast compression and detail enhancement, these methods maintain natural-looking scenes.
Many modern TVs and software players implement real-time HDR Tone Mapping, dynamically adjusting parameters per frame to deliver consistent, lifelike visuals regardless of on-screen brightness peaks or troughs.
Part 4. Frequently Asked Questions on HDR Tone Mapping
As HDR Tone Mapping becomes ubiquitous in TVs, monitors, and media players, users often have questions about its practical effects. The following FAQs address common concerns and misconceptions, covering everything from specific features to best-use scenarios. Whether you're comparing Dolby Vision to HDR Mapping or deciding whether to enable tone mapping for movies and games, these answers will guide you to optimal settings.
1. What does HDR tone mapping do?
HDR tone mapping compresses the scene's full luminance range into the display's capabilities, preserving highlight details and shadow nuances. It adjusts bright and dark regions differently often boosting midtones to create a balanced image that looks natural to the human eye. By doing so, tone mapping prevents washed-out whites and crushed blacks, enhancing overall contrast and color accuracy in HDR content.
2. Is Dolby Vision better than HDR tone mapping?
Dolby Vision uses dynamic metadata for per-scene or per-frame adjustments, which can outperform standard HDR tone mapping that often relies on fixed parameters. However, high-quality HDR Mapping algorithms, especially local operators can closely approximate Dolby Vision results. The advantage of Dolby Vision lies in its scene-by-scene adaptability, but robust HDR Tone Mapping implementations in modern TVs and software also deliver excellent performance without requiring specialized metadata.

3. Should HDR tone mapping be on for gaming?
Enabling HDR tone mapping in gaming ensures that bright explosions and dark corners maintain detail and visibility. It balances the extreme luminance peaks common in many modern games, providing a more immersive experience. While some players prefer the raw HDR output for maximum brightness, well-tuned HDR Mapping enhances both competitive visibility and cinematic immersion without introducing perceptible latency.

4. Is HDR tone mapping good for movies?
For cinematic content, HDR tone mapping preserves the director's intended contrast and color palette across various display types. With movies often graded for 1,000-10,000 nits peak brightness, tone mapping translates that to consumer screens (typically 300-1,000 nits) while maintaining mood and detail. Viewers benefit from richer blacks, vibrant highlights, and a faithful representation of on-screen visuals.
5. Should I turn off HDR tone mapping?
Turning off HDR tone mapping is generally not recommended unless your display natively supports the HDR peak brightness specified in the content. Without tone mapping, you'll encounter clipped highlights and lost shadow details on standard screens. If you notice unnatural contrast or color shifts, tweaking the tone mapping settings rather than disabling it entirely offers a better solution.
Bonus Tip. How to Get the HDR Videos With Upscaled HDR Effect?
For creators seeking to enhance their existing SDR footage with HDR-like brilliance, HitPaw VikPea offers an AI-driven solution. Its SDR to HDR Model intelligently expands dynamic range, boosts color depth, and refines low-light scenes to deliver a near-authentic HDR appearance. Whether you're working on vlogs, short films, or promotional videos, VikPea simplifies the process, requiring just a few clicks to transform ordinary clips into stunning visuals that rival true HDR content.
- AI-based SDR to HDR conversion for vivid color depth
- Enhanced contrast mapping to reveal hidden shadow details
- Low-light enhancement for clearer nighttime footage
- Dynamic luminance boosting without oversaturation
- Noise reduction preserving fine details in dark areas
- Batch processing to upscale multiple videos at once
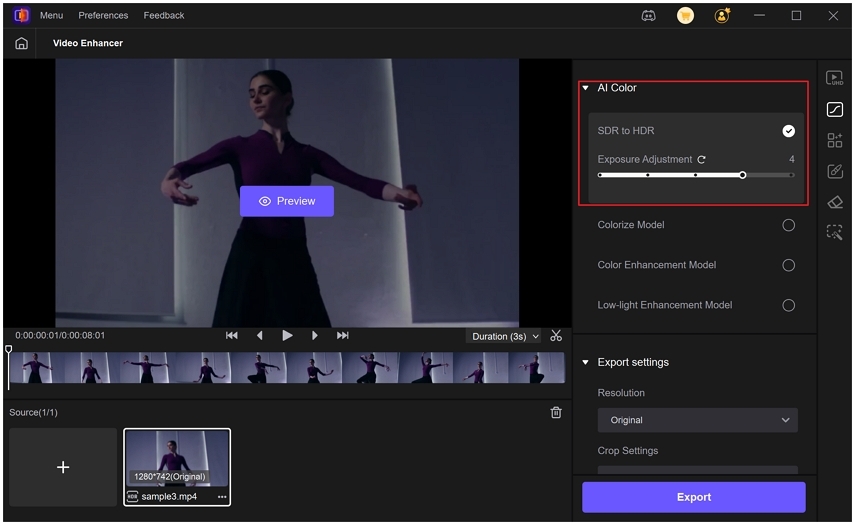
Step 1.Download and install HitPaw VikPea on your computer. Run VikPea after installing, click on AI Color and then click on SDR to HDR Model. Import the low-res videos you want to convert to HDR.

Step 2.Drag the slider to adjust the exposure level. The Exposure Adjustment slider in the SDR to HDR model lets you fine-tune the brightness level of your video after the dynamic range has been enhanced.

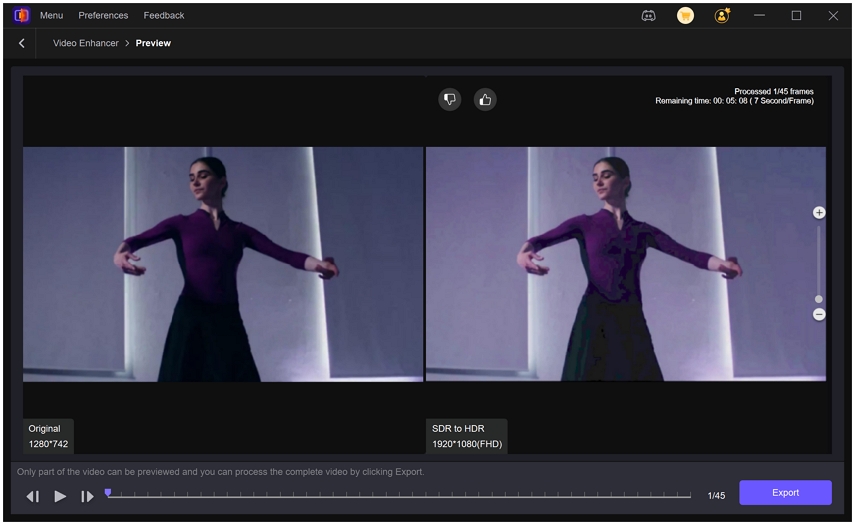
Step 3.Under Export Settings, choose your desired resolution. VikPea supports upscaling up to 4K or 8K. Preview the changes to see a side-by-side before-and-after comparison. Click on Export to transfer your color-balanced video to your computer.

Conclusion
HDR Tone Mapping and HDR Mapping play a pivotal role in modern content delivery, ensuring that high dynamic range footage looks its best on a variety of screens. By understanding the principles and choosing the right settings whether for gaming, movies, or professional work, you can unlock richer visuals, deeper contrast, and immersive experiences. And with tools like HitPaw VikPea, even standard SDR videos can attain stunning HDR-like quality, empowering creators and viewers alike.
Leave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles