What is Gaussian Noise? An In-Depth Guide to Help You Understand It
In the modern photography landscape, noise is a major concern for the creators. It harms your image quality, and sharing such images can be bad for your social media aesthetic. Gaussian Noise is a commonly seen error among the types of noise in images. To make your images worth sharing, you must get rid of this artifact. This guide explains what is Gaussian noise and how to enhance image quality affected by it.

Part 1. What is Gaussian Noise and The Concept Behind It
To answer the question, Gaussian noise is a type of distortion in images where pixel brightness changes randomly. These changes make some pixels appear slightly brighter or darker than they should be, creating a grainy texture in dark areas. Now that you know the Gaussian noise definition, the following list features the concept behind it:
1. Based on a Bell-Shaped Distribution: Most of the noise values are small, so the changes are often subtle and not too distracting. However, a few pixels may have larger changes, making them stand out unnaturally. This predictable distribution makes it easier for computer programs to detect and reduce the noise.
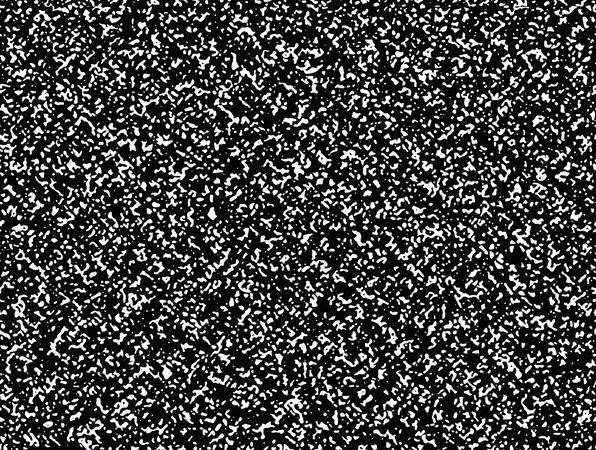
2. Common in Low-Light Photography: Gaussian noise is often seen in photos taken in low light or with low-quality cameras. In these conditions, the camera struggles to collect enough light, so it fills in gaps with random brightness values.

3. Makes Image Processing More Challenging: This noise can make it harder to understand what is in the image. That is why reducing Gaussian noise distribution is an important step in image editing and computer vision tasks.

Part 2. Role of Gaussian Noise in Image Processing and Artificial Intelligence
This type of noise in pictures can be used in image processing and AI in the following ways:
1. Object Detection: The presence of Gaussian noise reduces the clarity and accuracy of image-based analysis, such as object detection or facial recognition. This can be done by the grainy images it creates by randomly altering pixel brightness in low light.
2. Noise Reduction Techniques: To reduce the impact of Gaussian noise in images, various filtering techniques are used, such as Gaussian blur and median filters. The role of Gaussian noise is that it defines a problem that image processing techniques are specifically designed to solve.
3. Improving Generalization: In artificial intelligence, generalization refers to the model’s skill in handling previously unseen data. Gaussian noise in machine learning is useful in achieving this by forcing the model to learn more robust features and patterns.
4. Noise as a Regularizer in Deep Learning: Regularization techniques prevent the model from overfitting to the training data and encourage it to learn generalizable patterns. Applying Gaussian noise to the inputs or weights of neural networks is a strategy for regularization.
Part 3. What Are Different Types of Gaussian Noise
The concept of Gaussian noise is beyond a mere artifact. This diverse type of noise has various types, some of which are explained below:
1. Additive Gaussian Noise
It is used when Gaussian-distributed noise linearly alters a signal without any form of interaction or distortion. The values follow a Gaussian distribution with a zero average and a specified variance. This Gaussian noise example is used to model many natural and synthetic noise processes where interference overlays the original signal.
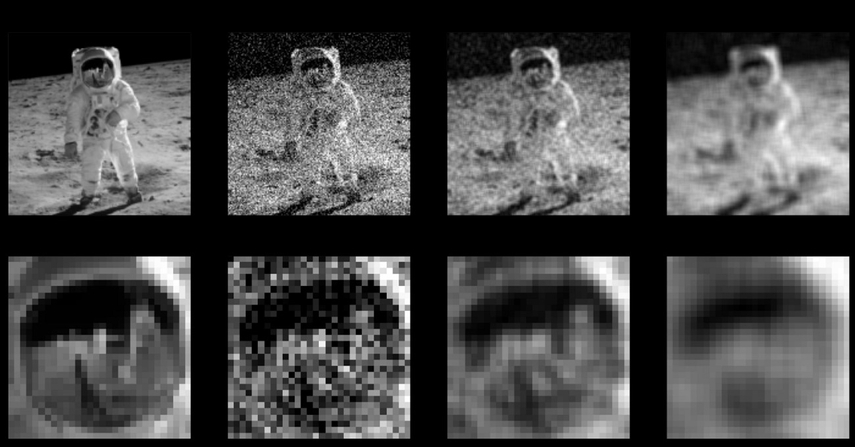

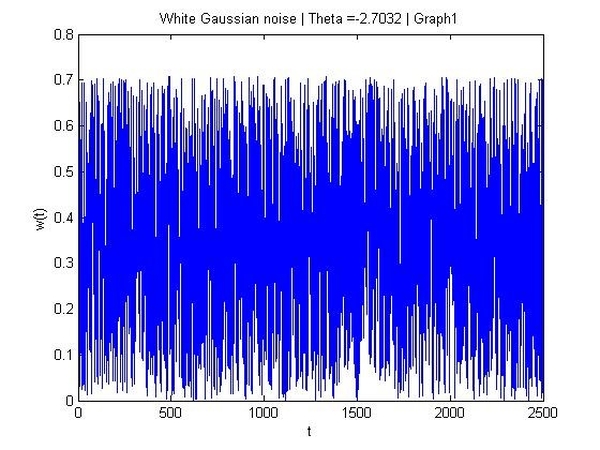
2. White Gaussian Noise
White Gaussian Noise combines a Gaussian amplitude distribution with uniform frequency power across a specified range. The name "white" is taken from white light, where all visible frequencies are present in equal amounts.
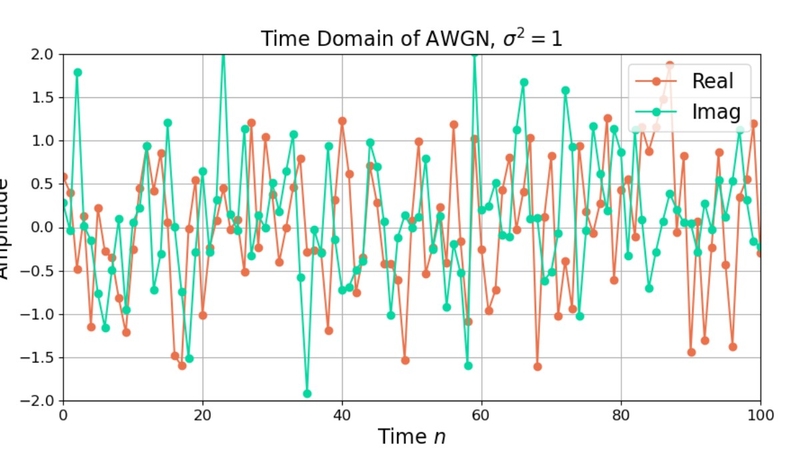
3. Additive White Gaussian Noise
The last type of noise is a blend of both types of noise, reflecting properties of both. It is the most common type in practical and theoretical scenarios because it simplifies analysis and often approximates real-world scenarios well. It is specifically helpful in scenarios like thermal noise environments or where no specific frequency component dominates the noise behavior.
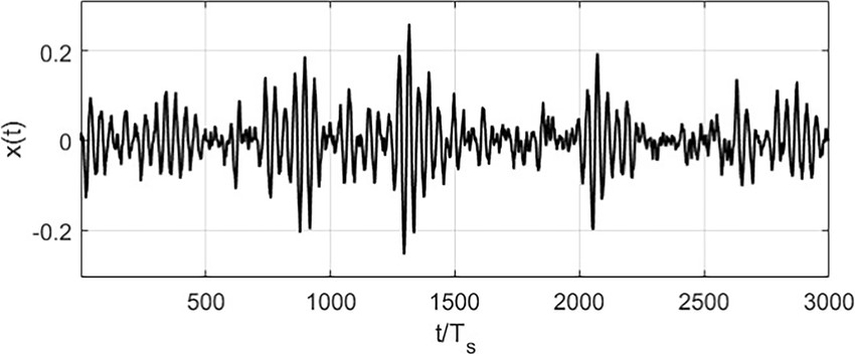
4. Multiplicative Gaussian Noise
Unlike additive noise, multiplicative Gaussian noise scales with the signal rather than being added to it. It models scenarios where the noise depends on the signal's amplitude, such as medical imaging.
5. Complex Gaussian Noise
This noise is represented as a complex number where both real and imaginary parts are Gaussian noise distributed. They are often assumed to be independent and identically distributed and are used in I/Q signals in communications and other complex-valued signal processing.
6. Correlated Gaussian Noise
In this type of noise, the noise samples are not independent and include temporal or spatial correlation. If adjacent pixels in imaging share similar noise characteristics, they still maintain a Gaussian distribution but with structured relationships between values.

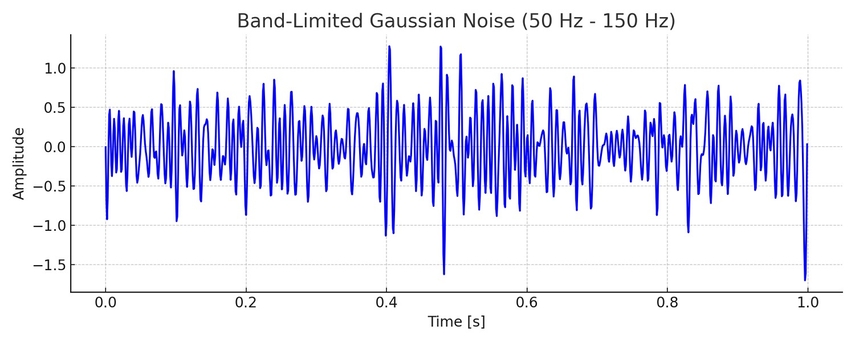
7. Band-Limited Gaussian Noise
Limiting it to a specific range of frequencies, this noise passes through a bandpass filter. It is common in communication systems where noise is only significant in specific frequency bands.
Part 4. Use Cases and Applications of Gaussian Noise in Various Fields
Until now, we have explored Gaussian noise in image processing as an error. The following points will explain the most common use cases of this noise that make it beneficial:
1. Image Processing: Gaussian noise is introduced during image capture in low-light conditions, where digital cameras struggle to gather light. It helps design filters for noise reduction, allowing clearer images to be obtained.
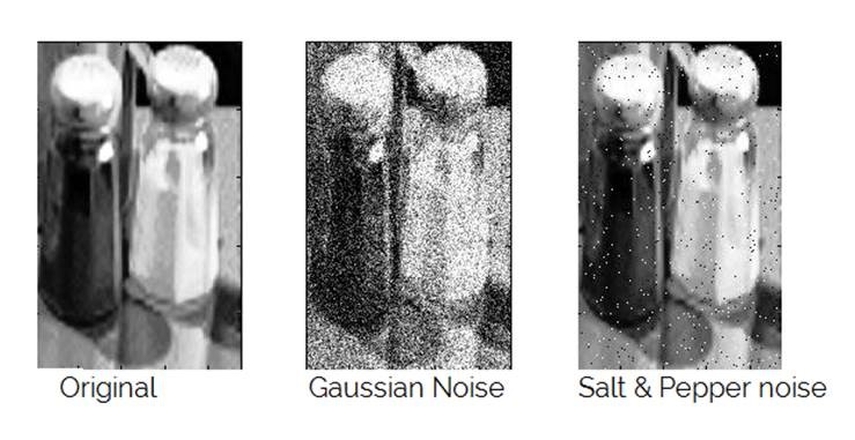

2. Data Augmentation for Training AI Models: In machine learning for image tasks, Gaussian noise is added to training images to help models learn to ignore irrelevant details and focus on key patterns. This technique improves the model’s ability to work with noisy images.

3. Real-World Imaging Conditions Simulations: It simulates image imperfections caused by low lighting or atmospheric conditions. Fields such as astronomy and surveillance rely on this due to the inherent noisiness of real data.
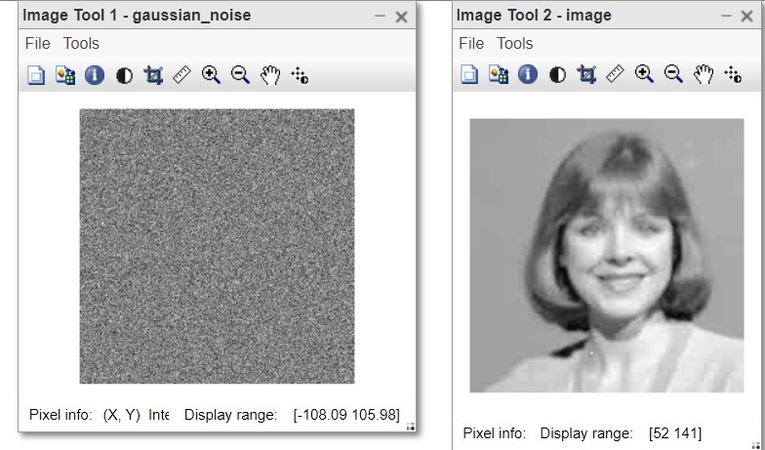
4. Performance Evaluation of Image Compression Techniques: Image compression algorithms are evaluated based on how well they preserve image quality when noise is present. Gaussian noise can intensify the weaknesses of a compression method if it introduces artifacts.
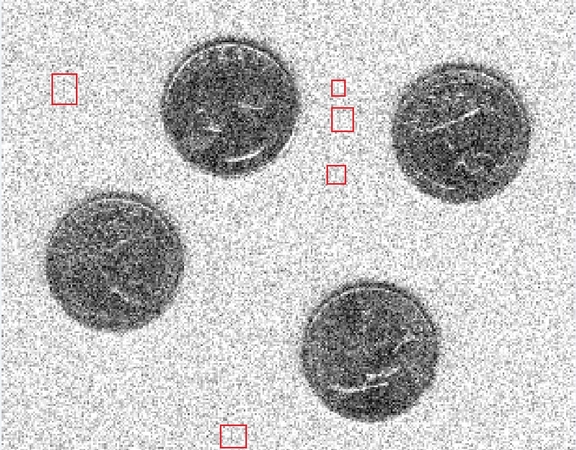
Part 5. Effectively Remove Gaussian Noise from Images via HitPaw FotorPea
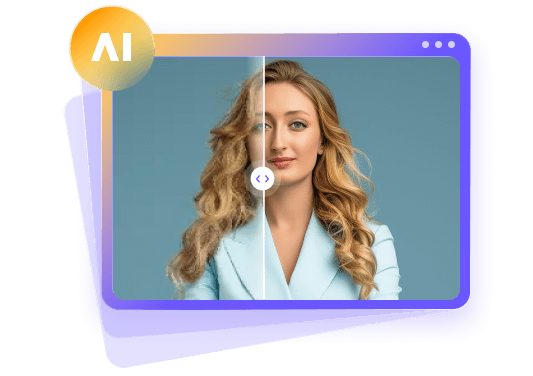
Imagine taking a picture of the moon and getting a noisy result with Gaussian noise characteristics. To make up for the bad quality of the picture, you will need an AI enhancer like HitPaw FotorPea. With its powerful enhancement algorithms, it restores the details of your image to produce an intricate result. If you want to upgrade the quality of a photo with faces, it will enhance your skin tone and refine the pores.
Besides importing a noisy image from the device, users can also use the sample photos to test the tool’s performance. This platform offers an extensive collection of AI models that can be used depending on the use case in each image.
A Quick Guide to Removing Gaussian Noise from Images Using HitPaw FotorPea
After understanding the capabilities of HitPaw FotorPea, let’s have a look at its step-by-step guide for Gaussian noise enhancement:
Step 1. Start by Accessing the Photo EnhancerTo start, open the tool on the desktop and select the “Enhance Photos Now” button to head to the next interface.
Step 2. Upload a Picture with Gaussian Noise
Now, select the “+” icon from the next interface to import a photo with noise.
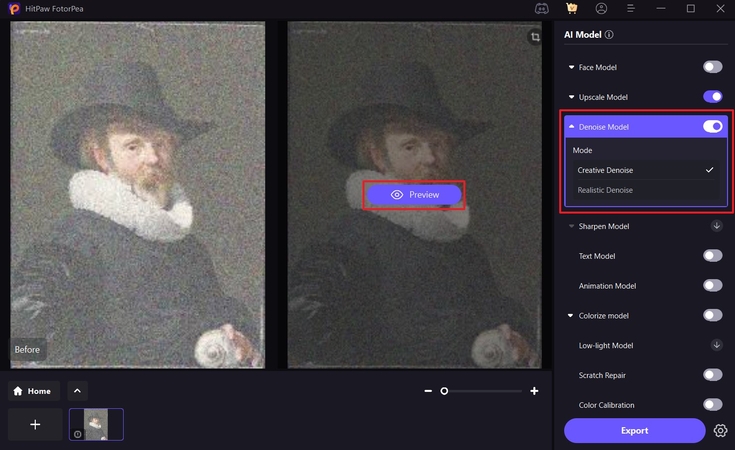
Step 3. Pick an Enhancement Model to Preview the Results
After importing the image, activate the "Denoise Model," choose an appropriate “Mode” for removing Gaussian Noise and click "Preview" to view the before and after results.
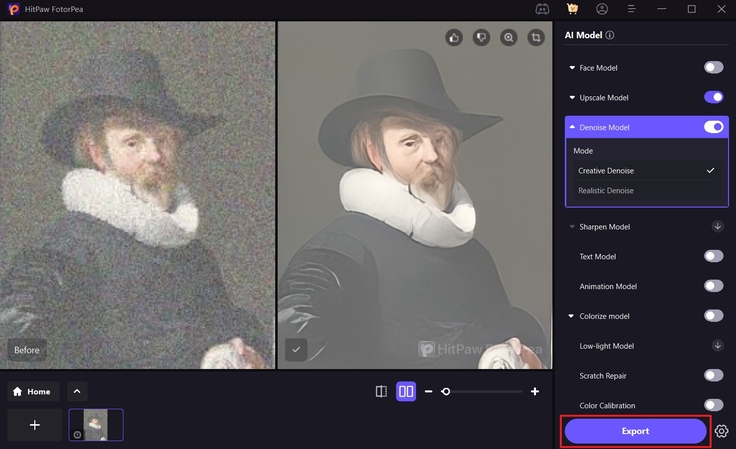
Step 4. Save the Enhanced Image to the Device
When you are finished enhancing the image, click the "Export" button at the bottom right to store it on your device.
Key Features
1. Auto Select Model: Users can enable the Auto Select Model option to let the AI detect the error in your image and suggest it accordingly.
2. Export Options: For better accessibility of the images, this tool allows you to export the images in JPG or PNG formats and high, low, or medium quality.
3. Robust Performance: Image enhancement is made quicker in HitPaw FotorPea thanks to the High-Res Acceleration feature.
Conclusion
Conclusively, this read answered the question of What is Gaussian noise and explored all its types. After giving you a complete insight into this error, we suggested HitPaw FotorPea as a robust image enhancer for pictures with Gaussian noise. With its numerous enhancement models, this platform refines the pixels of your photos and removes the artifacts.






 HitPaw Edimakor
HitPaw Edimakor HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer)
HitPaw VikPea (Video Enhancer) HitPaw Univd (Video Converter)
HitPaw Univd (Video Converter) 



Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Daniel Walker
Editor-in-Chief
This post was written by Editor Daniel Walker whose passion lies in bridging the gap between cutting-edge technology and everyday creativity. The content he created inspires the audience to embrace digital tools confidently.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles