MP3 vs M4A: Which Audio Format Should You Use?
When it comes to settling on a sound format, a lot of individuals would type in MP3 vs M4A. They are both popular, yet there are sound quality differences, file size and device support. The old is MP3 which can work almost anywhere and the new one is M4A which can offer a better sound quality in most occasions. In this article, the two formats are explained, the comparison and compatibility and licensing of these formats in the real-world setting is discussed and flexible tools that can be used to convert and manage audio files are introduced. You will come out of the reading with the best format that fits your needs
Quick Comparison Table: MP3 vs M4A
| Feature | MP3 | M4A |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Method | Lossy | Lossy (usually AAC) |
| Audio Quality | Good, can lose quality at low bitrates | Higher quality at smaller file sizes |
| File Size | Larger for same perceived quality | Smaller |
| Device Compatibility | Almost all devices and platforms | Strong on Apple devices, limited elsewhere |
| Metadata Support | Basic | Advanced |
| Licensing | Open and widely used | Restricted by Apple ecosystem |
| Typical Use Cases | Music sharing, offline playback | Streaming, Apple Music, podcasts |
Part 1: What the MP3 Format Is Used For
The MP3 is one of the oldest, as well as the most commonly used audio formats. It can be used in almost any device hence it is used in music, podcasts and audiobooks. MP3 is used to compress files to conserve space, and therefore, the files are smaller and can be easily shared. New formats do not make MP3 less popular as it is universal. Having been able to comprehend the advantages and shortcomings of MP3, you would be able to know when to use it on saving, sharing, and offline listening.

Advantages of MP3
MP3 is compatible with nearly all gadgets including smartphone, computer, and car audio. Easy to distribute over the web and store to vast collections. Offline playback is convenient since it does not need compression technology to reduce the file size significantly, thus making the file size smaller. Due to these characteristics, MP3 is the default to the general user and content producer.
Limitations of MP3
The MP3 file can be of low bit rate, which reduces the sound quality and blurred audio. MP3 is not as compressive as modern format and is also bulkier in size despite having similar quality sound. When making decisions of whether to use MP3 as a format of music or audio projects, the user ought to take into consideration the between the convenience and sound quality.
Part 2: Understanding the M4A Audio Format
M4A is a more recent audio format, most often paired with AAC encodings. Popular with Apple and streaming technology. M4A files have a superior sound quality as compared to MP3 files of the same size. M4A has become popular in the music, podcast, and online streaming. In comparison to MP3, compatibility is restricted, however, those listeners, who need a good sound quality, high storage capacity and the compatibility with the latest devices have the advantage.

Advantages of M4A
M4A files have a better sound quality, yet occupying less space. It is used to categorize music collections to store extensive metadata like album covers, track titles and artist information. Perfect as a default form of streaming services and Apple products. The compression technology is very efficient, providing an audio clarity at the moment of storage in large collections or at the moment of playing on the portable devices.
Limitations of M4A
M4A files cannot play in every device. Android smartphones with an older version, non-Apple devices and certain car audio systems might not work with M4A without extra software. There can also be problem in editing But to users who are more concerned about sound quality, where streaming and devices primarily use Apple devices, it is a powerful one M4A will perform better in audio and save capacity.
Part 3: MP3 vs M4A in Real-World Use
The choice of the MP3 and M4A vary depending on the application of the audio. Take into account the equipment, the storage space and the habits of listening. Whereas MP3 is compatible and easy to share, M4A has a higher sound quality and is smaller in terms of file size. The following section is a comparison of MP3 and M4A on a practical level to enable you to know which formats suit you in music and podcasts among other audio contents.

Audio Quality
M4A typically has a better sound compared to MP3 of the same bit rate. The compression technique preserves additional information, particularly vocals and instruments. The MP3 should be played with ease, although with low bit rates the sound can become flat. The M4A has a superior listening experience when clarity and loyalty are the priorities. But the standard of MP3 is normally good enough to play on simple devices on a daily basis.
Device Compatibility
The MP3 can work practically anywhere using smartphones to in-car devices to the old-fashioned media players. M4A is best compatible with Apple iPhone, iPad and Mac. Other devices that are not Apple might also need extra software or codecs. M4A has been primarily used on Apple devices and streaming services. The support of the devices is evaluated as one of the factors in choosing the formats to be used in music libraries and shared audio files.
Storage and Streaming
The M4A file has the same sound quality and less capacity than the MP3, saving storage capacity and bandwidth. This makes it ideal for streaming services and devices with limited memory capacity. Although the MP3 file has a large capacity, it is universal compatible and is suitable for offline use and sharing.
Choosing the Right Format
The choice is based on the priority. MP3 is certain in case you concentrate on compatibility and sharing. M4A is the choice to get a smaller file in a higher quality. Take into account your habits in using devices, storage, and listening and make a choice. It is common that many users keep both formats and listen to MP3 when in general and M4A when listening to high quality music.
Part 4: Compatibility, Licensing, and Practical Limits
MP3 and M4A are not equal in terms of licensing, support of devices, and utilization in the long run. MP3 is open and very compatible thus easy to share, edit and play anywhere. M4A relies on the Apple ecosystem, and therefore, there are certain devices that can restrict playback and editing. This section explains the process of licensing, compatibility, and practical aspects of the choice of the right format according to your needs.
MP3 Licensing
MP3 is open and free to use. You are able to share, edit and add it to your project online without the concern of issues to do with licensing. Such freedom renders MP3 the most suitable among the content creators, teachers and all those running huge libraries. MP3 licensing provides flexibility, making it a safe and convenient option for users seeking universal compatibility in playing, sharing and editing audio.
M4A Licensing
M4A is linked to Apple and its ecosystem. You can use it freely on Apple devices, but there may be restrictions on distribution and editing outside of the Apple platform. For some media players M4A additional software may be required for file playback. License restrictions affect users who want to share and edit M4A files across multiple platforms.
Long-Term Usage
MP3 is playable on almost all devices, ensuring long-term access. You can save, share, and convert files without worrying about compatibility. While M4A focuses on high sound quality, there can be problems with older devices and non-Apple platforms. It is important for music collectors and creators to consider long-term use. Many users hold MP3 for general-purpose access and M4A for high-quality listening.
Part 5: A Flexible Alternative for Audio Format Conversion
Both MP3 and M4A formats are widely used, but device limitations, personal listening preferences, and storage constraints often make switching between them necessary. Manually converting files can be tedious, time-consuming, and may reduce sound quality. HitPaw Univd offers a reliable solution, enabling users to convert, play, and organize multiple audio formats effortlessly. It preserves the original audio quality while providing an intuitive interface suitable for beginners and advanced users alike. With HitPaw Univd, your music library becomes more versatile, accessible across devices, and easier to manage without sacrificing audio fidelity.
Key Features of HitPaw Univd
- Audio Format Conversion: Easily convert MP3, M4A, and other popular audio formats while maintaining the original sound quality for versatile use across all devices.
- Batch Conversion Support: Convert multiple audio files at once, saving time and effort for large music libraries or extensive podcast collections efficiently.
- High-Quality Preservation: Maintain the clarity, depth, and richness of original audio files during the conversion process without any noticeable loss in quality.
- User-Friendly Interface: Navigate the simple and intuitive interface designed for both beginners and advanced users to convert and manage audio easily.
- Playback and Library Management: Play, organize, and manage your music collection on multiple devices anytime, ensuring easy access and smooth listening experience.
How to Convert MP3 to M4A Using HitPaw Univd
Step 1.Visit the official HitPaw website and download HitPaw Univd for your Mac or Windows. Follow the installation prompts to set it up quickly.
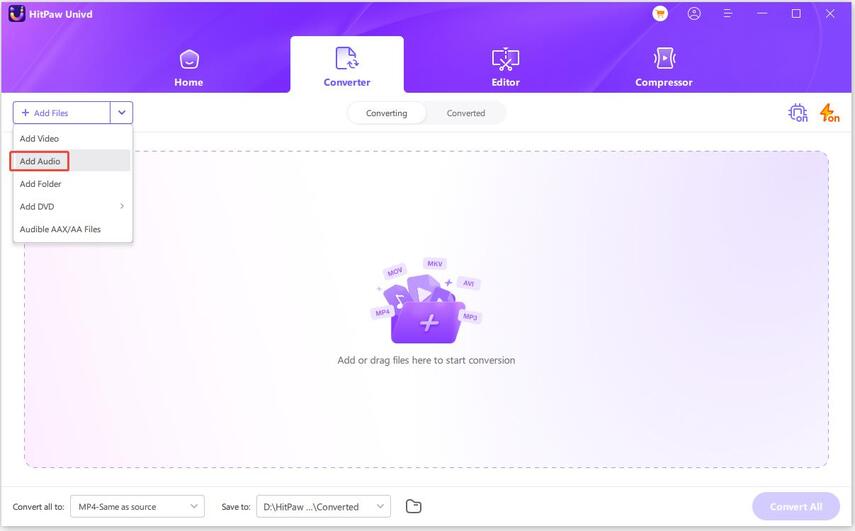
Step 2.Open the software and click Add Audio, or drag and drop your file. To extract audio from a video, use Add Video or drag the video file in.

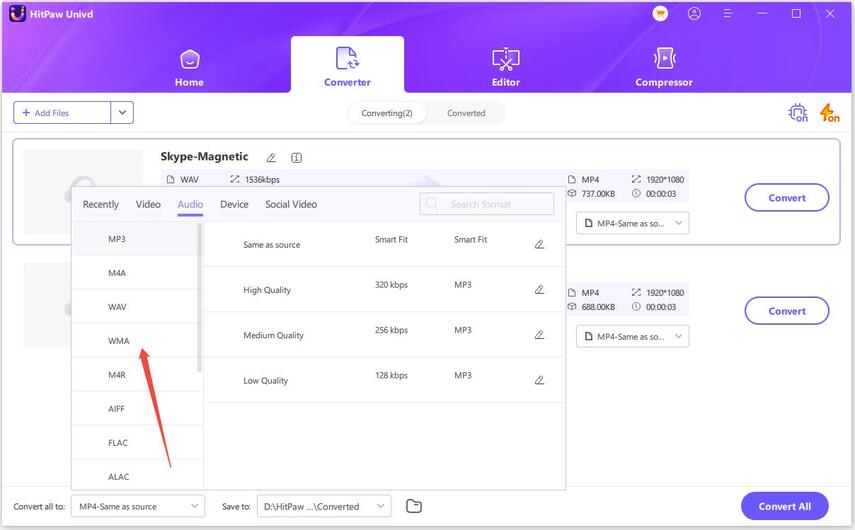
Step 3.Click the format icon next to each file or Convert all to for batch selection. Go to the Audio tab, pick a format (like MP3), and set the quality.

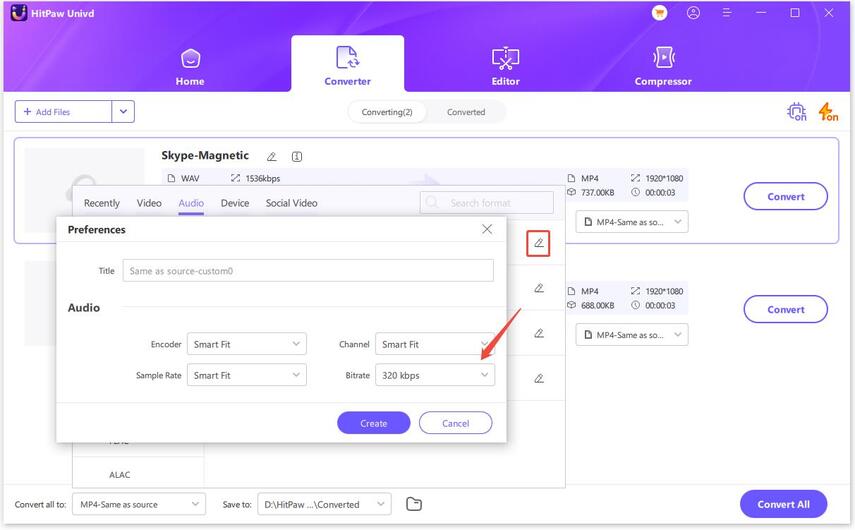
Click the edit icon to adjust parameters like bit rate or sample rate.

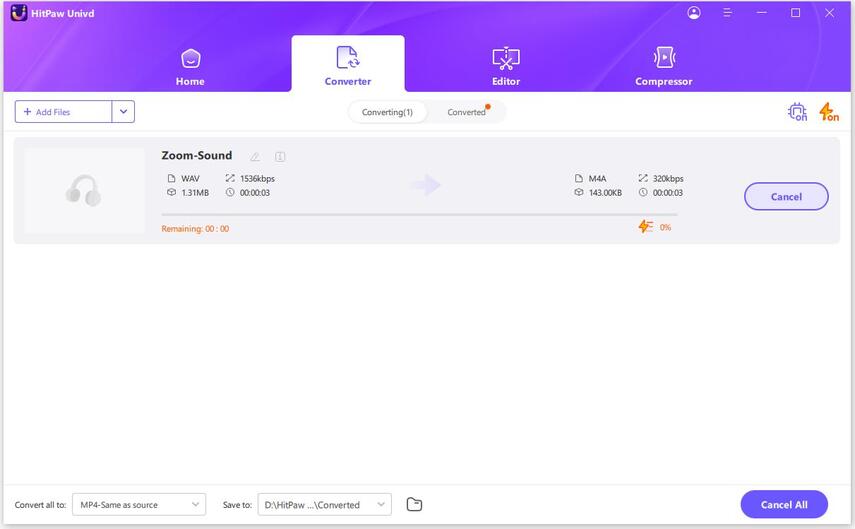
Step 4.Click Convert or Convert All to begin converting with lossless quality.

Step 5.Go to the Converted tab. Click Open Folder to view your files or Add to edit list for further editing.

FAQs about MP3 vs M4A
M4A usually offers higher sound quality at smaller file sizes compared to MP3. However, MP3 is more widely compatible with devices and platforms, making it a better choice when universal playback and sharing are priorities.
Yes, converting M4A to MP3 can reduce audio quality because MP3 uses a different compression method. Some details in vocals and instruments may be lost during conversion, so the final sound may not match the original M4A file.
Yes, MP3 files can be converted to M4A using tools like HitPaw Univd. While the format changes, the conversion won't improve the original MP3's quality it simply makes it compatible with devices supporting M4A.
Conclusion
Choosing between MP3 and M4A depends on your priorities and how you use audio files. MP3 is the most compatible format, working on nearly all devices and platforms, making it ideal for sharing, offline playback, and general use. On the other hand, M4A provides better sound quality at smaller file sizes, making it perfect for streaming, Apple devices, and high-quality listening. Understanding your needs, storage capacity, and device compatibility helps you make the right choice. For users who need flexibility, HitPaw Univd allows easy conversion, playback, and management of MP3, M4A, and other audio formats without losing quality.
Leave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles