MP4 vs MP3: Key Differences, Use Cases, and How to Convert
MP4 and MP3 are everywhere. You see them when downloading videos, saving music, or sharing media across devices. Because they're so common, many people assume they're closely related-or even interchangeable. In reality, MP4 and MP3 are designed for very different purposes.
This article helps you clearly understand what MP3 and MP4 mean, how they differ, and which format fits specific use cases best. We'll also explain why format conversion sometimes becomes necessary and how to manage both formats efficiently without technical complexity.
Part 1. What Are MP3 and MP4 Formats?
To the average user, the only difference might seem like a single digit, but under the hood, they belong to different families of technology.
What is MP3? (The Audio King)
MP3, short for MPEG-1 Audio Layer III, revolutionized the music industry in the 1990s. It was designed to compress audio data into small files while retaining sound quality that is nearly indistinguishable from a CD to the human ear.

Main features:
- Lossy Compression: It removes "invisible" sound data to shrink file sizes.
- Universal Compatibility: Works on everything from vintage iPods to modern smart fridges.
- Low Bandwidth: Ideal for fast streaming and quick downloads.
Best For: MP3 is ideal for music playback, podcasts, audiobooks, and background listening where small file size and wide compatibility matter more than perfect audio fidelity.
What is MP4? (The Multimedia Master)
MP4, or MPEG-4 Part 14, is a digital multimedia container format. Unlike MP3, which only holds audio, MP4 is like a "box" that can hold video, multiple audio tracks, subtitles, and even still images.
Main Features:
- Container Format: It houses different types of data streams simultaneously.
- High Compression/High Quality: It uses advanced codecs (like H.264 or H.265) to provide HD video at manageable sizes.
- Versatility: Supports interactive features and chapter markers.
Best for:
MP4 is best suited for videos, online streaming, social media content, online courses, and any scenario where visual and audio elements work together.
Part 2. MP4 vs MP3: Key Differences You Should Know
Although MP3 and MP4 are both media formats, they are built for different purposes. The table below highlights the most important differences at a glance.
| Feature | MP3 | MP4 |
|---|---|---|
| Media type | Audio only | Video + audio (multimedia container) |
| Compression type | Lossy audio compression | Efficient multimedia compression |
| File size | Very small | Larger than MP3 |
| Device & platform compatibility | Extremely wide | Very wide on modern devices |
| Best use cases | Music, podcasts, audiobooks | Videos, streaming, social media |
| Metadata support | ID3 tags (artist, title, album) | Detailed metadata (chapters, subtitles) |
MP4 vs. MP3 Quality: Video Experience vs. Audio Efficiency
When we talk about "quality," we have to look at what you are trying to achieve.
- MP4's Rich Experience: Because MP4 supports high-bitrate video and multi-channel audio (like 5.1 surround sound), it provides a complete sensory experience. If you want to see the artist perform while you hear the music, MP4 is the winner.
- MP3's Efficiency: MP3 is about "perceptual" quality. It uses smart logic to keep the sounds you actually hear and toss the rest. It is designed to be "good enough" for high-fidelity listening without eating up your phone's storage.
The Bottom Line: Bigger isn't always better. If you only need to listen to a lecture, an MP4 file is a waste of space. If you need the visual cues of a tutorial, an MP3 is useless.
Part 3. Advantages and Disadvantages of MP3 and MP4
Understanding the strengths and limitations of MP3 and MP4 helps users choose the right format based on real-world needs rather than assumptions.
MP3 Advantages
- Small file size: MP3 uses efficient compression to significantly reduce file size, making it ideal for storage-limited devices and fast online transfers.
- Wide support: MP3 files are compatible with almost all media players, operating systems, and devices, ensuring easy access everywhere.
- Optimized for audio-only use: Designed specifically for sound, MP3 is well suited for music streaming, podcasts, and spoken-word content.
MP3 Disadvantages
- Lower audio quality: Because MP3 uses lossy compression, some audio detail is permanently removed, which may not meet high-fidelity listening requirements.
- No video support: MP3 is strictly an audio format, making it unsuitable for any multimedia or visual content.
MP4 Advantages
- Highly versatile format: MP4 supports video, audio, subtitles, images, and chapters, making it suitable for a wide range of multimedia applications.
- Efficient compression: MP4 offers a strong balance between file size and quality, which is especially useful for streaming and online sharing.
- Rich metadata support: MP4 can store detailed metadata such as subtitles, chapter markers, and additional descriptive information, enhancing user experience.
MP4 Disadvantages
- Larger file size: The inclusion of video and additional data results in larger files, increasing storage needs and bandwidth usage.
- Greater complexity: MP4's flexibility can introduce challenges related to encoding settings, subtitle handling, and compatibility across older devices.
Part 4. Compatibility Issues with MP3 and MP4
In a perfect world, every file would work everywhere. In reality, you'll often find yourself with an MP4 video when you only need the audio for your gym playlist, or an MP3 that you want to upload to a video-centric platform like YouTube.
This is where compatibility issues drive the need for a professional management tool. HitPaw Univd is not just a simple converter; it is an all-in-one format management solution designed for both Windows and Mac users.
Feature Highlights:
- Lossless Extraction: Extract MP3 audio from MP4 videos without losing a drop of sound quality.
- Massive Format Support: Beyond MP3/MP4, it supports hundreds of video and audio formats.
- Batch Processing: Convert dozens of files simultaneously to save time.
- Video Compression: Compress large videos for easier sharing or perform quick edits before converting.
- Built-in AI Tools: Speech to text, noise removal, vocal remover, face blurring, etc.
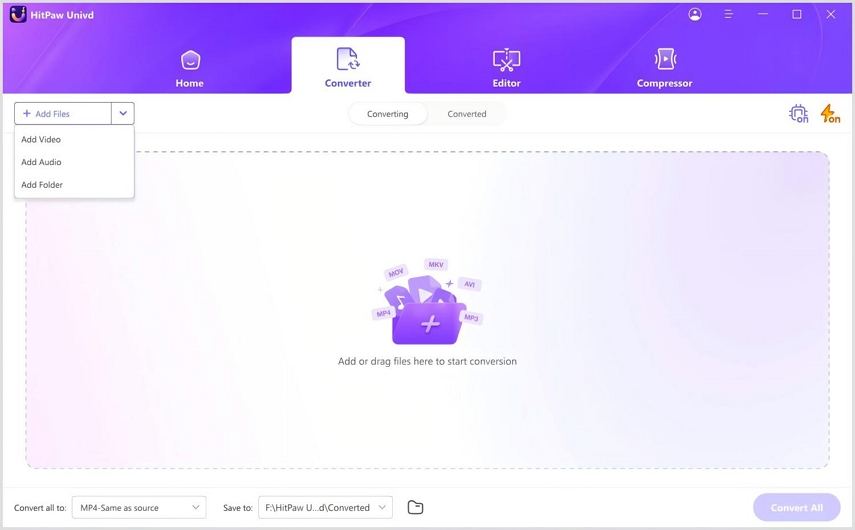
Step 1: Import Your Media
Launch Univd on your PC or Mac. Choose the Converter module and click on the "Add Video" or "Add Audio" button in the main interface. You can also simply drag and drop your files directly into the window. For efficiency, you can import an entire folder of MP4 files at once.
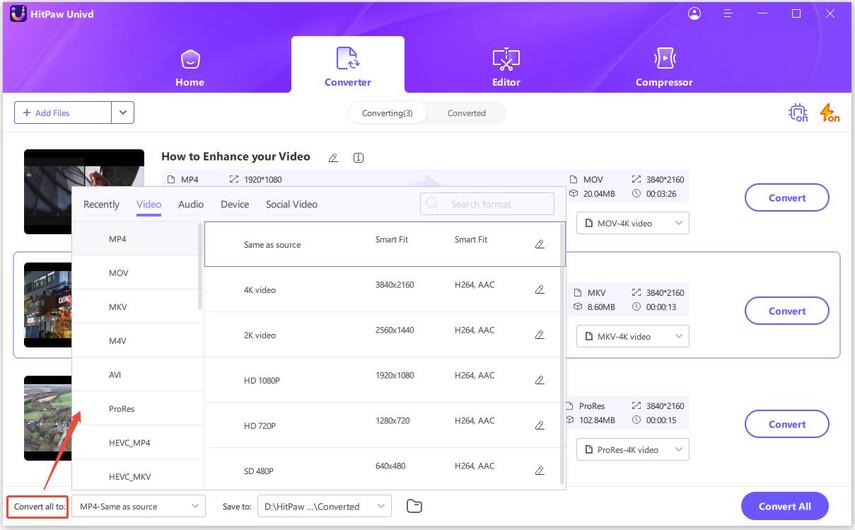
Step 2: Choose Your Optimal Output Profile
Navigate to the "Convert all to" option at the bottom or next to each file.
- To extract audio: Select the "Audio" tab and choose "MP3". You can further select the quality level (e.g., Same as Source, High Quality, or a specific bitrate in the format settings parameters).
- To create video: If you are turning an MP3 into a video for YouTube, select the "Video" tab and choose "MP4".
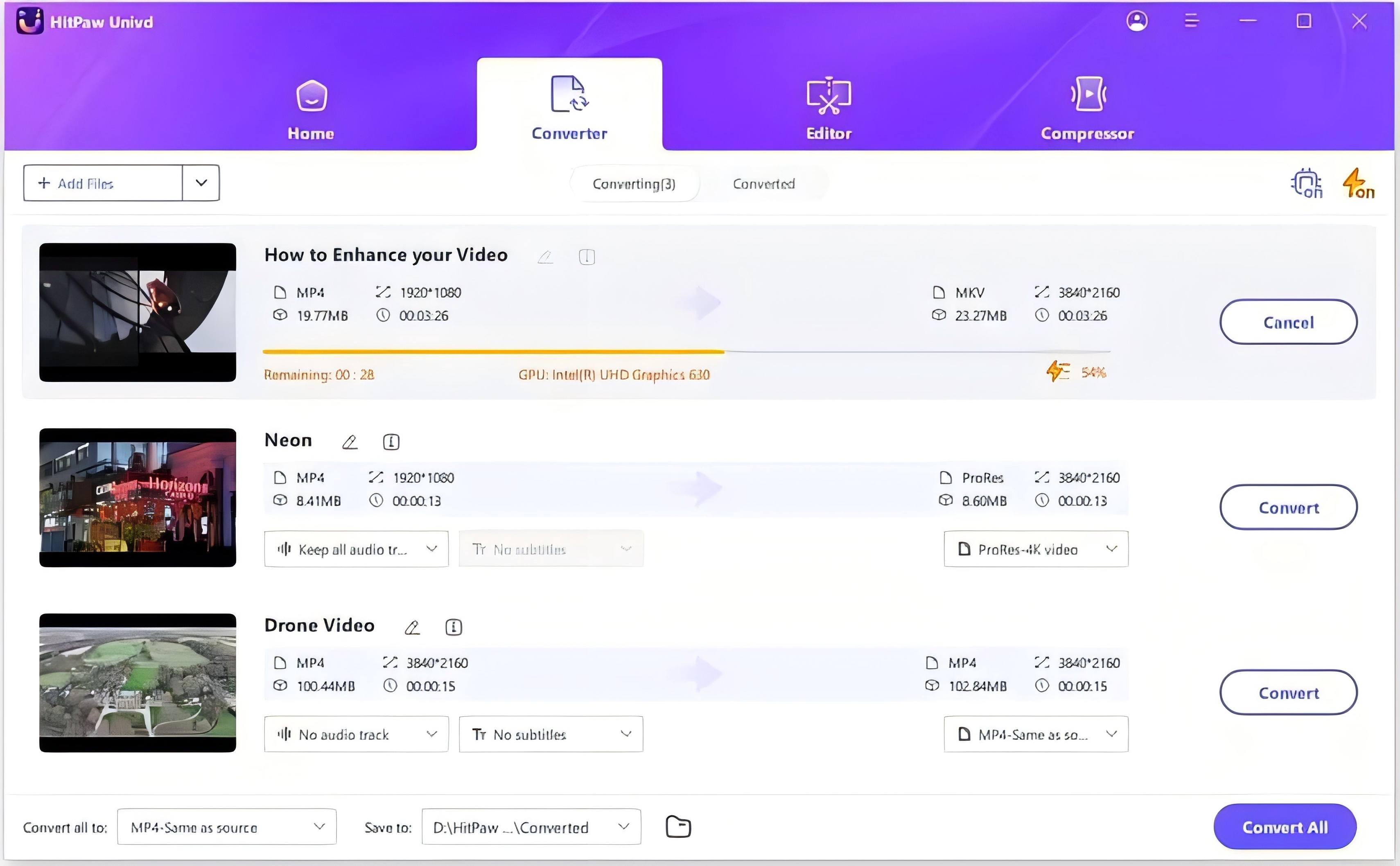
Step 3: Start Conversion
Once you are satisfied with the settings, click the "Convert All" button. Your new files will be ready in seconds in the designated output folder.
Part 5. MP4 vs MP3 FAQs
MP3 is better for audio-only use cases like music and podcasts due to its small file size and wide compatibility. MP4 is better for videos and multimedia content. Neither format is universally better-it depends on how you plan to use the file.
MP4 is a multimedia container that can include video, audio, subtitles, and metadata. While it's commonly used for video, it can also store audio-only content depending on how the file is created.
Most traditional MP3 players only support audio formats like MP3 and cannot play MP4 video files. Some modern devices labeled as "MP3 players" may support MP4, but this depends on the hardware and software.
MP4 audio can be high quality, especially when paired with modern audio codecs. However, MP4 is optimized for multimedia rather than pure audio efficiency, so file size is usually larger than MP3.
Yes, MP4 files can contain audio only. In such cases, they function similarly to audio formats, though MP3 is usually preferred due to better compatibility and smaller file size.
Conclusion
MP4 and MP3 serve different purposes, even though both are widely used. MP3 excels at audio efficiency and compatibility, while MP4 shines as a flexible multimedia format. Understanding their differences helps you choose the right format from the start.
When compatibility issues arise, tools like HitPaw Univd make it easy to manage, convert, and optimize your media files-ensuring they work wherever and however you need them.
Leave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles







