HDR10 vs HDR400: Key Differences, Features & Best Uses
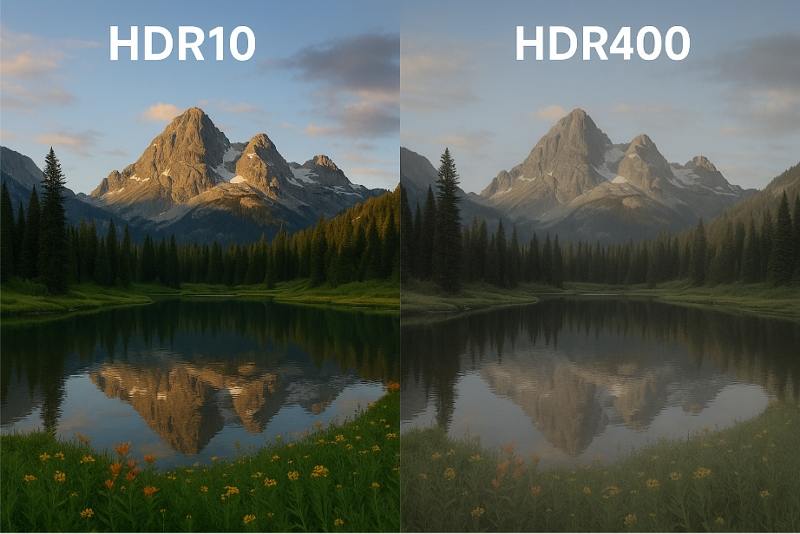
HDR10 and HDR400 are not competing HDR formats—they represent two very different levels of HDR performance. HDR10 is a true high dynamic range video standard used in TVs, consoles, and streaming platforms, while HDR400 is an entry-level display certification that mainly guarantees higher brightness than SDR.
In this guide, we break down HDR10 vs HDR400 across brightness, color depth, contrast, and real-world usage, and explain which one is better for gaming, movies, and everyday viewing. If you are choosing between an HDR400 monitor and an HDR10 display, this comparison will help you make the right decision.
Part 1. HDR10 vs HDR400: Quick Comparison (Summary Table)
| Feature | HDR10 | HDR400 |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Brightness | ≥1,000 nits | ≥400 nits |
| Color Depth | 10-bit (~1 billion colors) | 8-bit (~16.7 million colors) |
| Contrast Capability | High dynamic contrast | Limited by panel tech, no local |
| Metadata | Static metadata | None |
| Certification Standard | Industry HDR baseline | VESA DisplayHDR 400 |
| Target Devices | TVs, pro monitors, consoles | Entry-level monitors, laptops |
| Best For | Movies, pro video, high-end gaming | Everyday use, casual gaming, web browsing |
Part 2. What is HDR10?
HDR10 is an open HDR format that has become the industry baseline for high dynamic range video. By employing static metadata, HDR10 ensures consistent brightness, contrast, and color settings across entire videos. As the backbone of many modern TVs, monitors, and game consoles, HDR10 offers a balance of rich color expression and widespread compatibility. When assessing HDR10+ vs HDR400, HDR10's ability to deliver one billion colors and deep shadow detail makes it a popular choice for cinematic content and professional video work.
The Key Features of HDR10
- Rich color expression: Uses 10-bit color depth to render around 1 billion colors for smooth gradations and natural hues.
- High compatibility: Industry standard supported by most TVs, monitors, and consoles; ideal for movies and pro video production.
- Excellent light and dark detail: Enhances depth in shadows and highlights for a lifelike, dynamic image.
- Static metadata only: Applies the same brightness, contrast, and color settings throughout, unlike HDR10+ or Dolby Vision.
- Limited black level expression: Some LCD devices may struggle with deep darks, making HDR10 images appear flatter compared to OLED.
Part 3. What is HDR400?
HDR400 (VESA DisplayHDR 400) is often considered a “basic HDR entry point” rather than a true HDR experience. While it guarantees higher peak brightness than standard SDR displays, it does not require local dimming, wide color gamut, or true 10-bit color depth.
As a result, many HDR400 displays deliver brighter images but limited contrast and color depth compared to HDR10-capable TVs or monitors. HDR400 is best viewed as a brightness certification, not a full HDR video standard.
The Key Features of HDR400
- Increased brightness: Ensures at least 400 nits of peak brightness for vibrant highlights in bright environments.
- Bright enough for general use: Ideal for rooms with ambient light; enhances contrast in movies, games, and web browsing.
- Wide compatibility: Certified across many gaming monitors and laptops, supporting most HDR10 content sources.
- Limited color depth: Generally capped at 8-bit, reproducing about 16.7 million colors, less than HDR10's 10-bit palette.
- Contrast limitations: Dynamic range depends heavily on panel tech; may lack deep shadow detail compared to higher HDR standards.
Part 4. HDR10 vs HDR400: Key Differences Explained
When evaluating HDR 400 vs HDR 10, key factors such as brightness, color depth, contrast, metadata handling, and device support come into play. This section dives into seven core areas where HDR10 vs HDR400 diverge, helping you decide if an entry-level HDR400 monitor meets your needs or if you should invest in a true HDR10-qualified display.

1. Brightness Standard
HDR10: Supports over 1,000 nits peak brightness for vibrant highlights in challenging lighting.
HDR400: Entry-level HDR standard requiring a minimum of 400 nits, suitable for casual viewing.
2. Color Depth
HDR10: Utilizes 10-bit color depth, displaying over one billion colors for smooth gradients.
HDR400: Typically 8-bit support, rendering approximately 16.7 million colors.
3. Contrast Ratio
HDR10: Designed for higher contrast ratios, revealing fine detail in shadows and highlights.
HDR400: Dynamic contrast is limited and often hinges on panel technology and local dimming.
4. Types of Metadata
HDR10: Uses static metadata, no scene-by-scene brightness or color optimization.
HDR400: No metadata concept; focuses solely on display brightness and color gamut.
5. Authentication
HDR10: Widely adopted HDR standard supported by TVs, monitors, and streaming platforms.
HDR400: Certified under VESA DisplayHDR 400 with lower performance requirements.
6. Supported Devices
HDR10: Broad support across high-end TVs, gaming monitors, and professional displays.
HDR400: Common in entry-level monitors and laptops requiring basic HDR compatibility.
7. Intended Use
HDR10: Ideal for cinematic experiences, advanced gaming, and professional video production.
HDR400: Best for light gaming, web browsing, or casual media viewing.
Comparison Table of Differences Between HDR10 and HDR400
Part 5. How to Convert SDR to HDR Video with AI
While HDR10 requires compatible displays and properly mastered content, many users still watch SDR videos on HDR screens. This often results in flat contrast and muted highlights—even on HDR10 displays. HitPaw VikPea helps bridge this gap by converting SDR footage into HDR-style video, allowing HDR displays to better utilize their brightness and color capabilities. This is especially useful when playing legacy or online videos on HDR10 or HDR400 monitors.
- Instantly transforms low-quality into 4K quality.
- Enhances shadow detail in underexposed scenes for clearer images.
- Expands color gamut for richer and more natural hues.
- Supports up to 8K export for ultra-sharp playback.
- Convert multiple videos simultaneously with fast AI acceleration.
- Fine-tune brightness post-conversion for perfect balance.
- Compare before and after in real time to ensure quality.
- Choose resolution, format, and codec in a single interface.
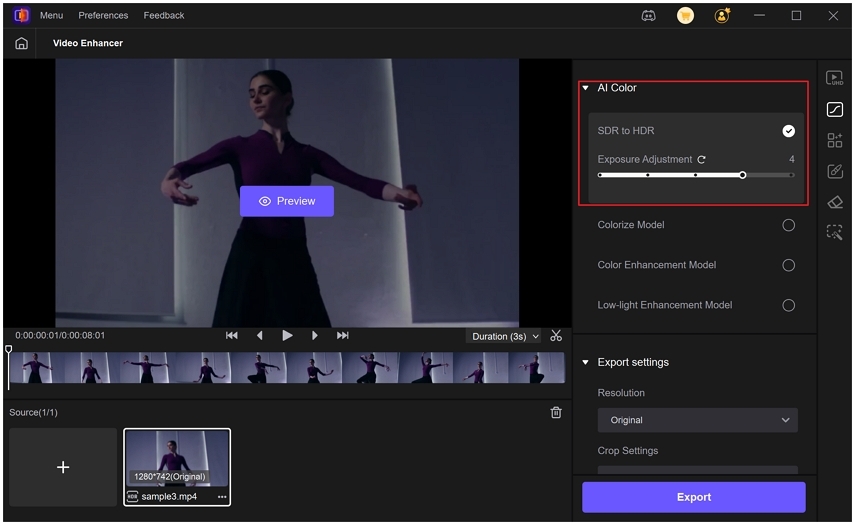
Step 1.Download and install HitPaw VikPea on your computer. Launch the app, select AI Color, then click on SDR to HDR Model. Import your video file.

Step 2.Adjust exposure using the Exposure Adjustment slider to fine-tune brightness after dynamic range enhancement.

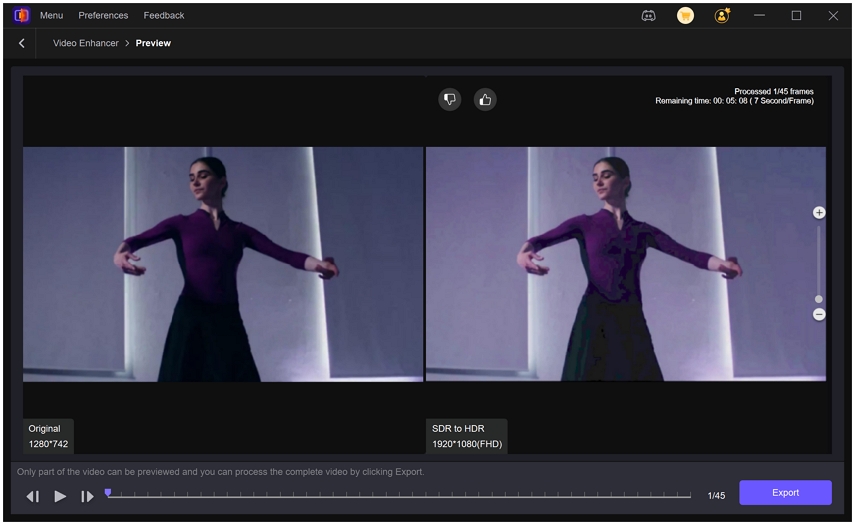
Step 3.Under Export Settings, select your desired resolution (up to 4K or 8K). Preview the result in the side-by-side window, then click Export to save your HDR-enhanced video.

Part 5. Frequently Asked Questions on HDR10 and HDR400
Yes, HDR10 is better than HDR400 in overall image quality. HDR10 supports higher peak brightness, true 10-bit color depth, and wider dynamic range, allowing HDR content to display with richer colors and stronger contrast. HDR400 is an entry-level display certification that mainly increases brightness and delivers limited HDR performance.
Dolby Vision and HDR10+ are among the top HDR standards, featuring dynamic metadata and up to 10,000 nits peak brightness in supported content.
Yes. HDR10 provides excellent color depth and contrast for gaming, especially on high-end monitors and TVs that exceed 1,000 nits peak brightness.
HDR400 does make a difference compared to standard SDR by providing higher peak brightness, which improves highlight visibility in bright environments. However, it does not offer true HDR contrast or color depth. The visual improvement is noticeable but limited, especially when compared to HDR10-capable displays.
Conclusion
HDR10 and HDR400 are designed for very different use cases. HDR10 is a true HDR standard that delivers higher brightness, richer colors, and better contrast for movies, gaming, and professional viewing. HDR400, by comparison, is an entry-level display certification that improves brightness but offers limited HDR depth. To get the best visual experience, your display capability and content quality must align. When HDR content is unavailable, AI-based SDR-to-HDR enhancement tool like HitPaw VikPea can help HDR displays perform closer to their full potential.
Leave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles