What Is Film Colorization and How Black and White Movies Were Colorized?
Film colorization transforms monochrome footage into vibrant color, helping modern audiences connect with classic films and historical footage. This process blends art and technology, requiring knowledge of period palettes, lighting, and photographic nuance. Whether restoring family archives or preparing archival material for museums and streaming platforms, colorization can enhance storytelling without erasing original intent. This guide explains traditional techniques, modern AI approaches, tool recommendations, and practical workflows you can apply to your projects.
Part 1. What is Film Colorization?
Film colorization is the process of adding or recreating color in originally black and white motion pictures. It involves choosing appropriate colors for skin, clothing, skies, and sets while maintaining the original lighting and texture. Colorization can be used for restoration, historical presentation, education, or creative reinterpretation. Done well, it preserves the film's character while making visuals more accessible for contemporary viewers who expect color imagery.
Part 2. How Black and White Movies Were Colorized?
Before AI, colorization relied on human artists and frame-by-frame techniques to assign color values. The process demanded careful research into period-accurate hues and manual work to maintain natural transitions across motion and cuts. Here is how the process usually works, step by step:
- Research and reference gathering to determine historically accurate colors and materials.
- Frame selection and keyframe planning to set color anchors across scenes.
- Rotoscoping and matte creation to isolate subjects, backgrounds, and elements per frame.
- Color mapping by assigning base color fills to each matte or layer.
- Layer blending and lighting adjustments to match original grayscale luminance and contrast.
- Color grading to unify the scene palette and preserve mood and atmosphere.
- Frame-by-frame touch ups to correct spill, motion blur, and edge artifacts.
- Compositing and final render to produce a continuous colorized video sequence.
Part 3. How Are Black and White Movies Colorized with AI?
AI film colorization uses trained neural networks to predict plausible colors from grayscale input, learning from large datasets of color footage. This approach dramatically reduces manual labor and speeds up the workflow while delivering natural-looking results. Modern AI colorizers like HitPaw VikPea can identify skin tones, vegetation, skies, and fabrics, and can maintain temporal consistency across frames. It offers dedicated AI colorization models and processing pipelines for both simple and intensive restoration work.
- Automatic color grading tuned for natural skin tones and historic accuracy.
- AI driven colorization that preserves original lighting and cinematic contrast.
- Noise reduction and detail refinement to restore texture while avoiding over smoothing.
- Upscaling engine to increase resolution with minimal artifacts and sharp edge recovery.
- Batch processing and GPU acceleration for fast colorization on large film archives.
- Real time preview and frame comparison to adjust results before final export.
How to do film colorization with HitPaw VikPea Video Enhancer?
Step 1.Download and install HitPaw VikPea on your computer. Run VikPea after installing, click on the "AI Colorist" feature on the main interface.

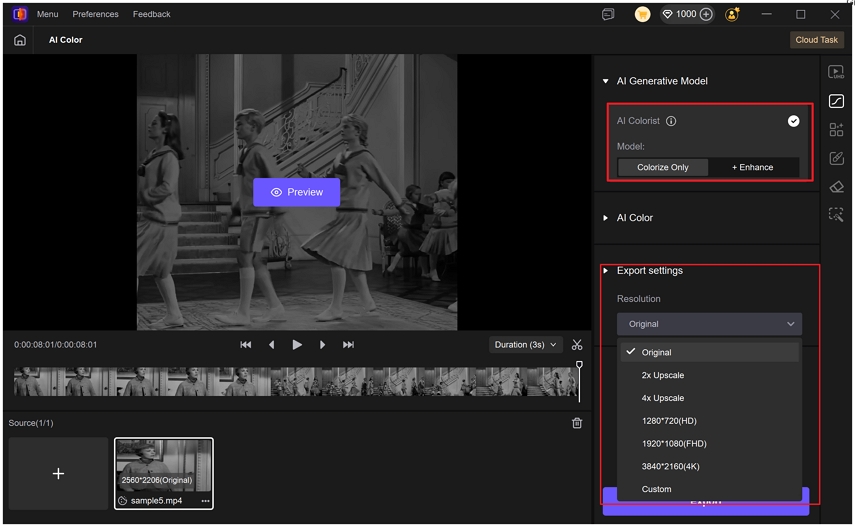
Step 2.Import the file you want to colorize. The AI Colorist provides two specific models for different video types:
Colorize Only: This model adds natural, AI-generated colors to your footage while keeping the original resolution and sharpness unchanged. The default resolution for this model is original, but you can also select a higher resolution in the Export Settings.

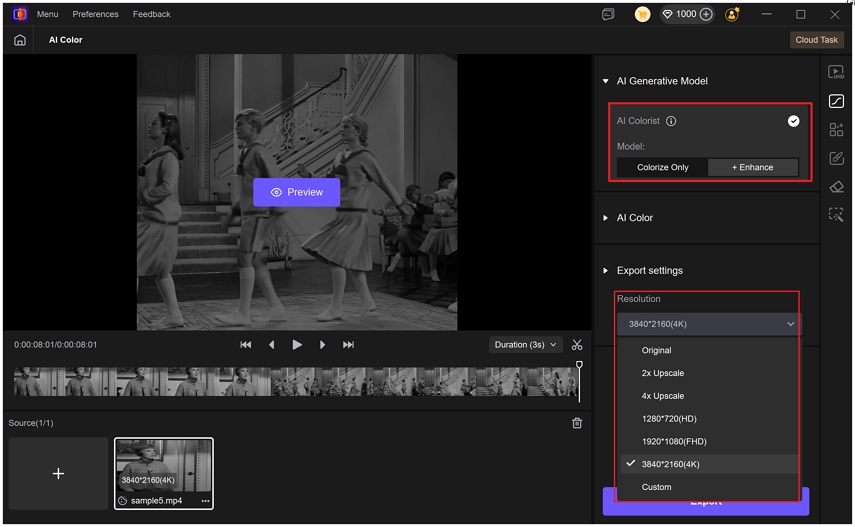
Colorize + Enhance: This model adds color and applies VikPea's enhancement engine to upscale resolution, reduce noise, and refine details for a crisper, more vivid result. The default export resolution for this model is 2x upscale, you can choose a higher resolution up to 4K in the Export Settings.

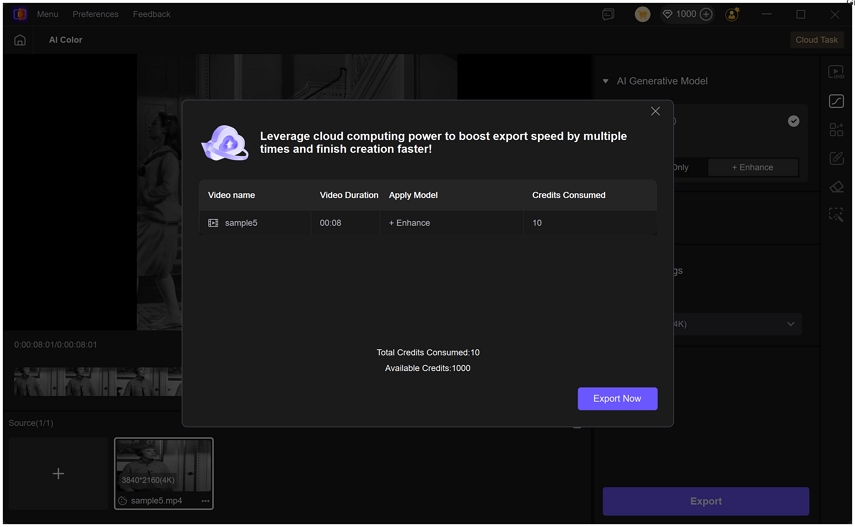
Step 3.Preview the changes to see how your improved colors look in your video. Now, once you have your colorized, click on "Export" to transfer your color-balanced video to your computer.

Step 4.When the process is completed, you can open the output folder and play the video with color and quality improvement.

Part 4. Traditional Film Colorization vs. AI Automatic Film Colorization
Comparing traditional methods and AI driven colorization highlights trade offs between human judgment and automation. Traditional methods excel in artistic control and historical fidelity when skilled artists are involved. AI methods excel in speed, consistency, and scalability while producing very good results with less manual labor. The right choice depends on project scale, budget, desired control, and archival standards.
Category
Traditional Film Colorization
AI Automatic Film Colorization
Technique Used
Manual rotoscoping, hand painting, keyframe color assignments
Neural networks, deep learning color prediction, temporal smoothing
Quality
High when done by experts, with nuanced artistic control
High for many scenes, improving rapidly with modern models
Time
Very time consuming, often many hours per minute of footage
Much faster, often minutes to hours per clip depending on resolution
Cost
High labor cost due to skilled artist time
Lower labor cost, but requires compute resources and software
Expertise and Skills
Requires colorists, historians, rotoscope artists, and compositors
Requires technical operators and post editors for final tuning
Accuracy
Potentially very accurate with research and human judgment
Generally accurate, may require human correction for rare cases
Best For (Uses)
Prestige restorations, historical accuracy where fine control is needed
Large archives, rapid colorization, and preliminary restorations
Scalability
Limited by manual labor and time
Highly scalable with batch processing and GPU acceleration
Control and Flexibility
Maximum control over exact hues and artistic choices
Good flexibility with faster iterates, some manual tweaking needed
Preservation Standards
Compatible with archival standards when documented
Can meet preservation needs if metadata and original are retained
Part 5. Frequently Asked Questions on Film Colorization
Yes. AI can colorize old movies effectively by predicting natural colors and applying temporal consistency, though human review improves historical accuracy and details.
AI delivers high accuracy for common subjects like skin and foliage. Rare colors and historically specific hues may need manual correction for precise authenticity.
Time varies by length, resolution, and workflow. AI can colorize minutes to hours of footage quickly, while full manual restoration may take weeks or months.
Conclusion
Film colorization bridges historical preservation and contemporary viewing preferences. Traditional methods remain valuable for high fidelity restorations where artistic control is paramount. AI driven colorization offers a fast, scalable alternative that brings many classic films and archives to modern audiences with striking results. Combining AI tools such as HitPaw VikPea with human oversight yields the best balance of speed, cost, and authenticity. If you have specific footage you want to colorize, testing a short clip is the fastest way to evaluate quality and plan the full restoration workflow.
Leave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles