Motion Compensation in Video: A Deep Dive and Review
To ensure your video takes up less space, you usually use a technique of motion compensation by using data from previous frames to predict future frames. This technique not only divides frames into fixed-size blocks but also makes your video appear as a checkerboard-like pattern, particularly in areas with smooth gradients. To help you avoid it from impacting your video quality negatively, we discuss it in detail in our article, along with the related terminologies.
Part 1. Understanding Motion Compensation & Related Terminologies
Let’s explore motion estimation and motion compensation in detail by understanding related terminologies:
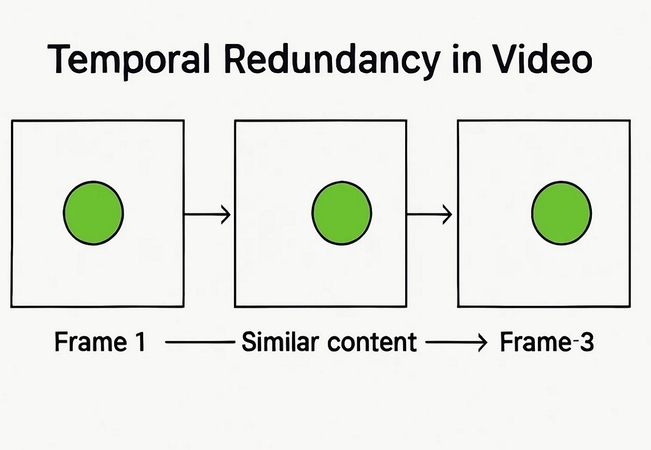
Temporal Redundancy
Temporal redundancy in a video means that the successive scenes in a video sequence have similar visual information. Removing it is significant for compressing a video efficiently, removing large amounts of redundant data, and making your video load faster.
Reference Frames
Here’s what role each reference frame plays in video compression:
- I-Frame: I-frames are self-contained keyframes that hold all image data for that specific moment.
- P-Frame: This kind of frame stands for predicted frame and tells about the upcoming changes forward.
- B-Frame: B-frames achieve the highest compression by estimating both forward and backward changes from surrounding I and P frames.
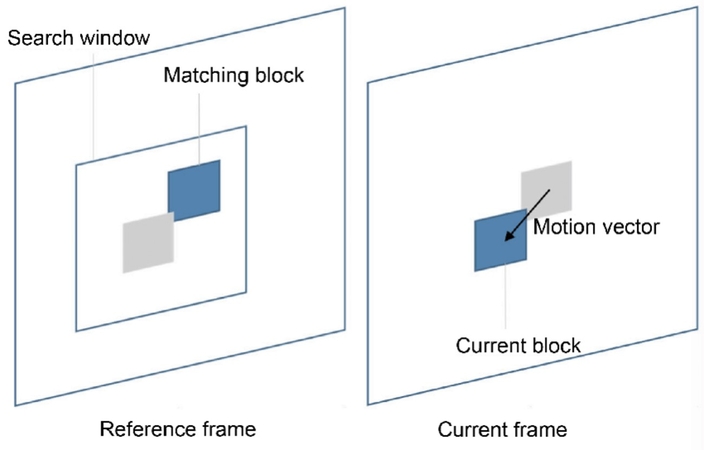
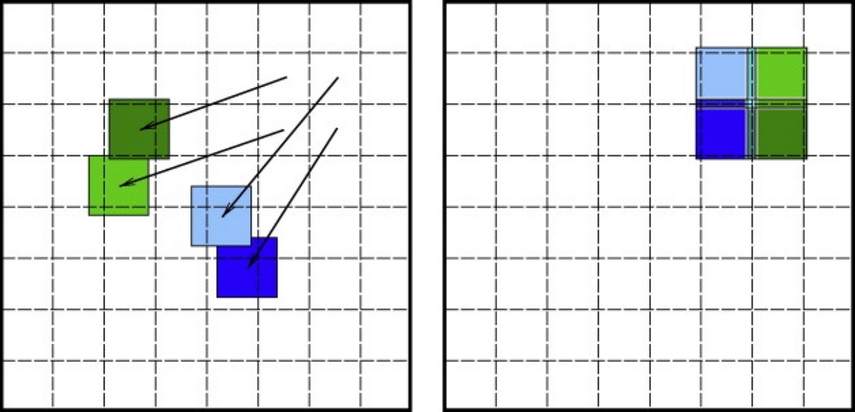
Block-Based Motion Estimation
This motion compensation VR technique divides video frames into small fixed macrosquares. Moreover, the encoder looks for a “search window” in the reference frame to find a similar block. For instance, in full search, the algorithm checks every possible block within the search window. However, a diamond-shaped pattern of search points is used in the diamond search, and a hexagonal pattern is used in the hexagon search.
Types of Compensation
- Forward vs. Backward Prediction: In forward prediction, you predict a block by looking at the preceding reference frame, but in backward prediction, you predict a block by looking at the succeeding block.
- Bi-directional Motion Compensation: In bi-directional motion compensation, you predict a block by using the information from both preceding and succeeding reference frames.
Part 2. Motion Compensation in Emerging Applications
Having discussed its types and related terminologies above, let’s explore the camera motion compensation in emerging applications now:
1. AI-Enhanced Video Compression
AI algorithms improve motion estimation and compensation accuracy, which results in efficient compression and fewer artifacts.
2. Game Streaming and Cloud Gaming
Highly efficient motion compensation helps you minimize latency and deliver smooth gameplay by compressing streamed video frames quickly.

3. Augmented Reality (AR) / Virtual Reality (VR)
With this, you can maintain visual stability and reduce motion sickness by accurately predicting user head movements for a consistent virtual environment.
4. Medical Imaging
In medical imaging, we use it to correct for patient motion during scans, such as ultrasound, and improve image clarity by stabilizing the visual data.
Part 3. Benefits and Drawbacks of Adopting Motion Compensation
After discussing its use in emerging applications, let’s have a look at the benefits and drawbacks of adopting motion compensation:
Benefits of Adopting Motion Compensation
Anyone who adopts motion compensation will get these benefits:
- Dramatically reduces video file sizes by eliminating the redundant information between frames.
- Enables smoother streaming and faster transmission of video content over networks.
- Ensures a natural viewing experience by predicting and compensating for motion.
Drawbacks of Adopting Motion Compensation
Like everything else, adopting motion compensation also has the following drawbacks:
- Both encoding and decoding processes need power to process, especially the advanced algorithms.
- Imperfect motion prediction leads to visual distortions such as blurring or blocking.
- In applications like live streaming, in order to analyze and predict frame things get delayed.
Part 4. Modern Implementations With Motion Compensation
Below are the modern implementations with VR motion compensation along with their examples:
In Video Codecs
Let’s first understand their role in video codecs:
1. H.264/AVC: Utilizes variable block sizes (from 16x16 down to 4x4) to accurately capture motion in different areas of the frame. For instance, a small bird flying will use smaller blocks and sub-pixel accuracy for its wings, and this way, its flight will appear smooth.
2. H.265/HEVC: This codec introduces techniques like advanced motion vector prediction and merge/skip modes to guess information from the surrounding blocks. For example, you can skip or merge a large static background area with a reference block to save bandwidth.
3. AV1 and VVC: They use highly advanced features such as multi-reference prediction and overlapped block motion compensation (OBMC/0 to smooth out edges between predicted blocks.
Hardware Acceleration
In VR motion compensation, these specialized hardware units offload the demanding computations of motion estimation and compensation from the CPU. For example, when you stream a 4K Netflix movie, your graphics card’s NVDEC 9NVIDIA), or Quick Sync (Intel), performs the heavy lifting of decompressing the video with its motion compensation features.
Part 5. Fix Motion Compensation Artifacts in Videos with HitPaw VikPea
Motion compensation isn’t always perfect and can cause video shaking, blocky patches, or ghost shadows, especially when you pause or slow down the footage. These problems make the video look unstable and less clear. HitPaw VikPea’s (formerly HitPaw Video Enhancer) Stabilize Model automatically fixes shaky motion and removes these artifacts, creating smooth, stable videos.
Key Features
1. The Stabilize Model removes distracting video shake and motion artifacts, delivering smoother and more stable footage.
2. Using the Denoise Model, all sorts of noise within the compressed video is nullified for getting a smooth video output.
3. The Video Quality Repair Model fixes all the imperfections within the compressed video and return a restored version.
4. With the Face Model, you can specifically enhance the facial details within your compressed video to highlight all involved individuals.
5. Bring back the actual colors of the video using the Colorize Model, which returns with a sharp video.
Steps To Remove Video Artifacts From Video With VikPea
The following steps guide you on how to minimize motion compensation VR from your videos using HitPaw VikPea:
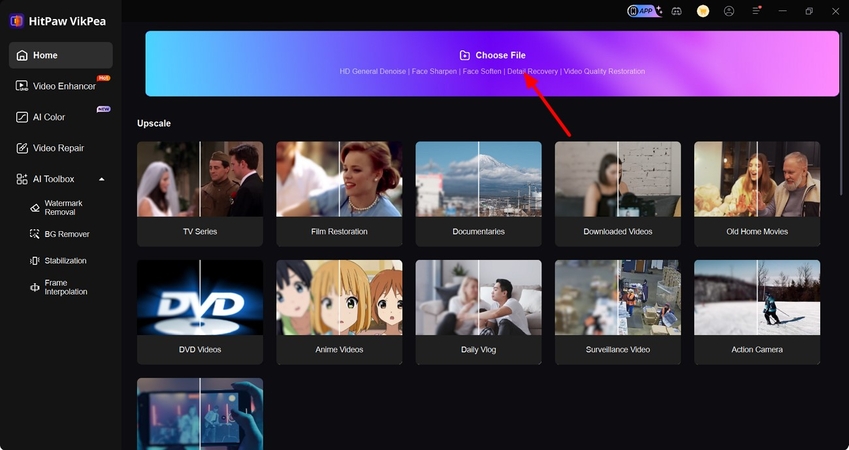
Step 1. Open HitPaw VikPea and Add a Clip With ArtifactsTo initiate, open HitPaw VikPea on your PC and hit the “Choose File” option from the Homepage to import a clip with artifacts.
Step 2. Access VikPea’s Stabilize Model
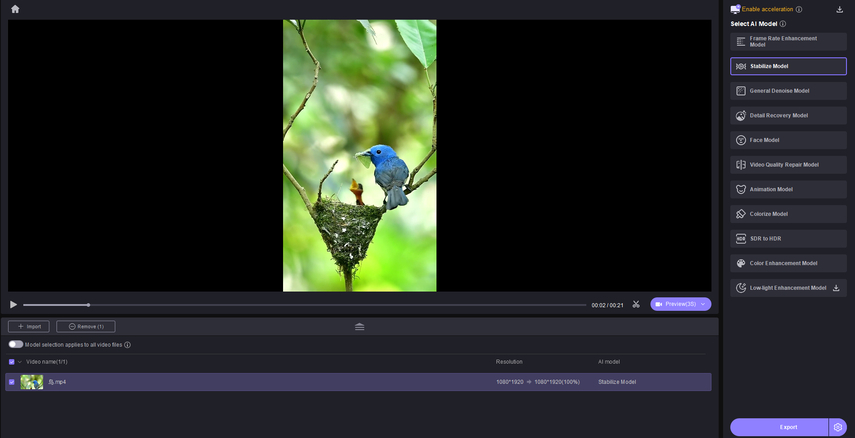
Next, access VikPea’s “Stabilize Model” from the right side and hit the “Preview” button to check the results.
Step 3. Export Your Artifacts Removed Video
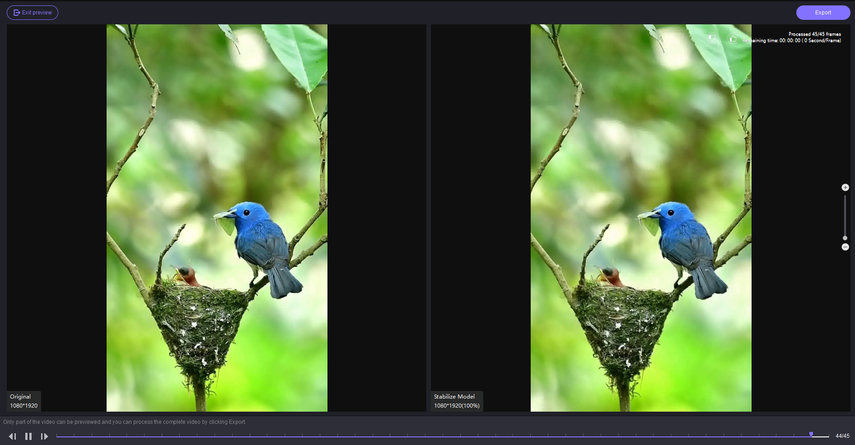
Finally, when the tool displays results with the artifacts removed from your clip, click the “Export” button in the top-right corner to save it to your device.
Part 6. FAQs on Motion Compensation
Q1. What should you know about SRS Motion Compensation?
A1. SRS (Stereotactic Radiosurgery) is a technique in medical imaging that tracks and corrects patient movement during the treatment.
Q2. What is the difference between motion compensation and motion estimation?
A2. Motion compensation involves using those calculated motion vectors to predict the content of the current frame, and motion estimation includes identifying and calculating the movement of blocks between video frames.
Q3. What is motion compensation in video compression?
A3. It is a technique that reduces video file size by predicting parts of a new frame based on the previous frames' content and movement.
Q4. What is a motion vector in video compression?
A4. A motion vector is a numerical representation (like an arrow) that shows the displacement of a block of pixels from its position in a reference frame to the new one.
Q5. What compression is best for video?
A5. The best compression depends on the specific application and file size, but you can maximize it with HitPaw VikPea’s video quality repair model.
Conclusion
To conclude, this article discussed motion compensation in detail, including its types and emerging applications. It focused on a solution, HitPaw VikPea, that contains a video quality repair model, which you can use to fix your clips. With VikPea, you can remove artifacts and noise that occur due to compression and improve your overall video quality.








 HitPaw Edimakor
HitPaw Edimakor HitPaw FotorPea
HitPaw FotorPea HitPaw Univd (Video Converter)
HitPaw Univd (Video Converter) ![6 Best AI Face Punch Generators on PC & Online [2026 Guide]](https://images.hitpaw.com/topics/ai-video/ai-face-punch-cover.jpg)



Share this article:
Select the product rating:
Daniel Walker
Editor-in-Chief
This post was written by Editor Daniel Walker whose passion lies in bridging the gap between cutting-edge technology and everyday creativity. The content he created inspires the audience to embrace digital tools confidently.
View all ArticlesLeave a Comment
Create your review for HitPaw articles